Figure 3.
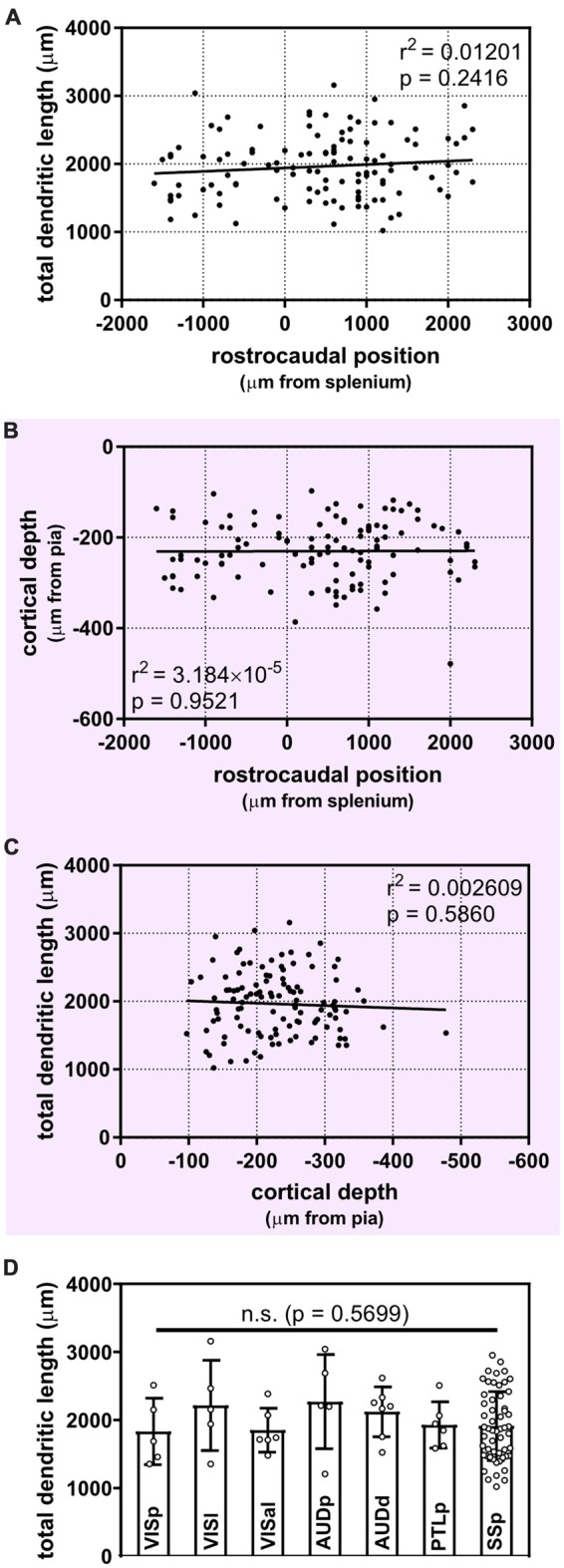
Uniform morphological heterogeneity in supragranular pyramidal neurons across the rostrocaudal axis, cortical depth and functional regions of the mouse. (A) No apparent relationship between the position of neurons along the rostrocaudal axis and their total dendritic length (linear regression). (B) Cortical depth of targeted supragranular cells does not appear to differ systematically across the rostrocaudal axis of the mouse cortex (linear regression). (C) No apparent relationship between depth of supragranular neuron and total dendritic length (linear regression). (D) No inter-regional differences observed across targeted regions (Kruskal-Wallis with Dunn’s multiple comparisons). VISp, primary visual area; (N = 5 neurons), VISl, lateral visual area; (N = 5), VISal, anterolateral visual area; (N = 6), AUDp, primary auditory area; (N = 5), AUDd, dorsal auditory area; (N = 7), PTLp, posterior parietal association area; (N = 6), SSp, primary somatosensory area; (N = 55). One neuron in ectorhinal cortex and 1 neuron in supplementary somatosensory area were not included in analysis. For (A–C), N = 116 neurons.
