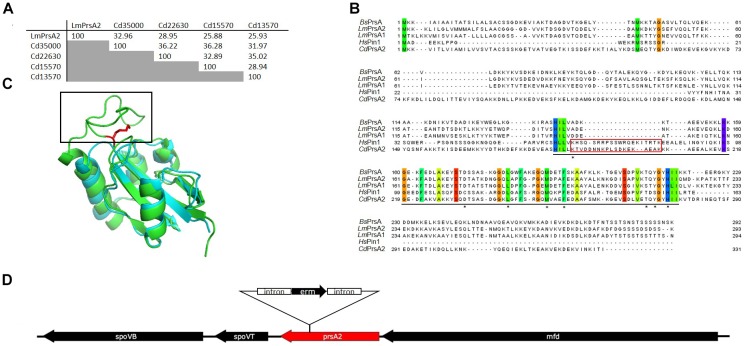
FIGURE 1.
CD630_35000 is the closest homolog of PrsA2 of L. monocytogenes in C. difficile with unique features. (A) Similarity analysis of all putative parvulins of C. difficile with the virulence associated parvulin LmPrsA2 of L. monocytogenes shows that CD630_35000 (CdPrsA2) displays the highest similarity to LmPrsA2. (B) Alignment of amino acid sequences of CdPrsA2 (Q180Z8), LmPrsA1 (Q71ZM6) and LmPrsA2 (Q71XE6) of L. monocytogenes, BsPrsA (P24327) of B. subtilis and HsPin1 (Q13526) of humans reveals highly conserved amino acids, especially in the PPIase domain (underlined). The alignment was performed using the T-Coffee webserver and visualized by Jalview 2.10.3b1. Amino acids that are conserved to 100% are highlighted by color coding according to Taylor (Taylor, 1986; Notredame et al., 2000; Waterhouse et al., 2009). Amino acids that have been mutated in CdPrsA2 for enzymatic studies are marked by an asterisk. A variable loop that aligns with the human HsPin1 and is absent in all other bacterial PrsA proteins is highlighted in red. (C) Structural alignment of HsPin1 (pdb:1NMV) and BsPrsA (pdb: 4WO7) reveals a loop (highlighted in red) in the human parvulin that has no homology in BsPrsA but aligns with CdPrsA2 (see also B). Shown in red is the side chain of the catalytically important amino acids K63 in HsPin1 that corresponds to K188 in CdPrsA2. (D) Shown is the genetic localization of the 996 base pairs long ORF of CD630_35000 (CdPrsA2) in the genome of C. difficile strain 630Δerm with the integration site of the ClosTron construct between bases 262 and 263. Shown are also the downstream adjacent genes spoVB and spoVT as well as the upstream adjacent gene mfd.