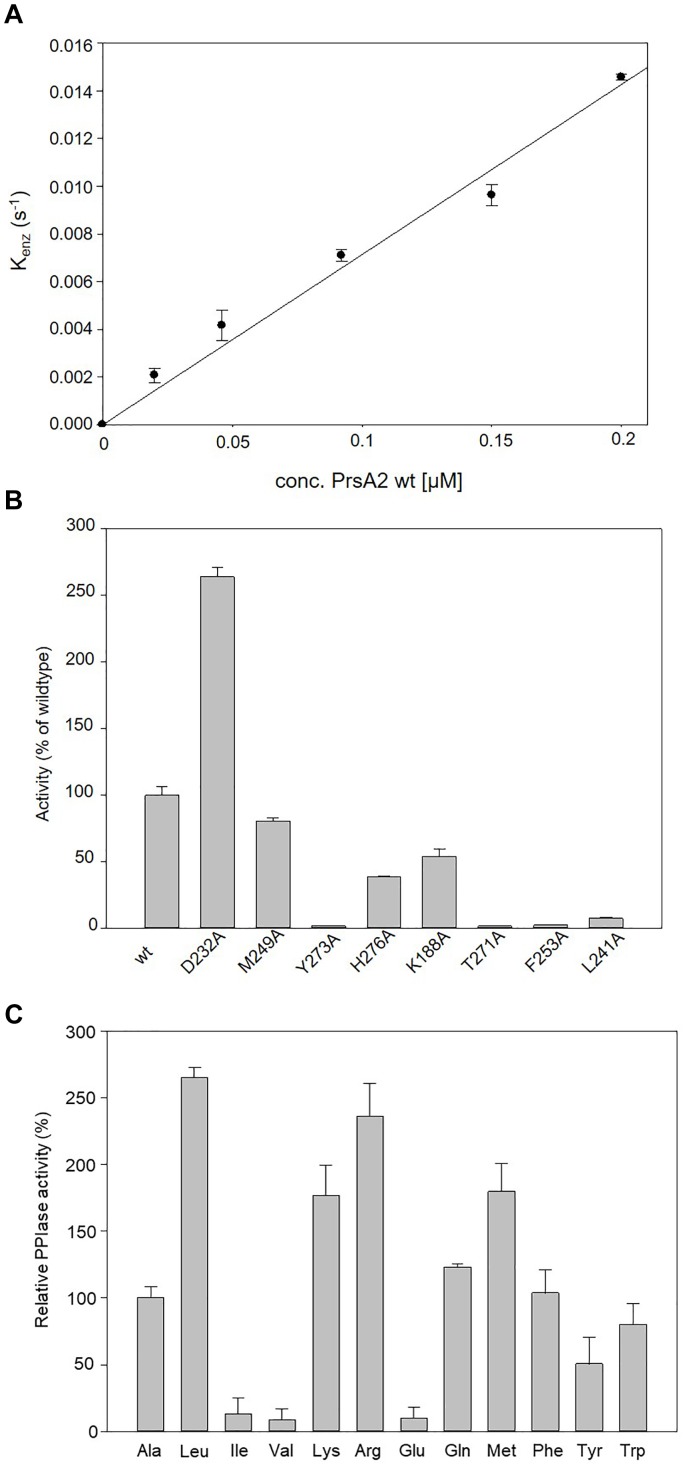
FIGURE 2.
PPIase activity profile of CdPrsA2. (A) Determination of the catalytic efficiency of wtPrsA2 (kcat/Km 6.78 × 104 M-1 s-1) by evaluation of the linear dependency of kenz from the concentration of the protein. The cis/trans isomerization of the PPIase substrate Suc-Ala-Ala-Pro-Phe-pNA was measured by the protease-free PPIase activity assay. The time courses were followed using a HP 8452 diode array spectrophotometer at 330 nm after jumping from the peptide stock solution in LiCl/TFE into the final buffer solution at 10°C. Measurements were done in 35 mM HEPES pH 7.8. Each data point represents the mean of three independent measurements. (B) Substitution of selected conserved amino acids in the PPIase domain by alanine revealed that especially the amino acids in the catalytic core Y273, T271, F253 and L241 are involved in the PPIase activity. Substitution of Y273 and T271 reduced the catalytic efficiency to 1.5% of the wild type protein, whereas the alanine substitutions of F253 and L241 yielded catalytic efficiencies of 2.3 and 7.4%, respectively. Moderate changes were observed when M249 or H276 were replaced by alanine, which decreased catalytic efficiencies to 80.5 and 38.5%, respectively. Replacement of the non-canonical K188 by alanine yielded a variant with only 53.8% residual efficiency. Substituting D232 by alanine resulted in 264% increased PPIase activity compared to wild type protein. (C) Relative PPIase activities of CdPrsA2 for substrates with different amino acids N-terminal to proline compared to its activity towards Abz-Ala-Ala-Pro-Phe-pNA. Determination of kcat/Km was performed by evaluation of the linear dependency of kenz from the concentration of CdPrsA2. Catalytic efficiencies were increased to 264, 236, or 176% for substrates with leucine or the positively charged amino acids arginine or lysine preceding proline, respectively. In contrast, the catalytic efficiency dropped to 9.9% or to 8.4%, when substrate peptides containing glutamate or valine were used, respectively. Data are means and SEM of three independent measurements. Statistical significance was determined by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), (∗p ≤ 0.05).