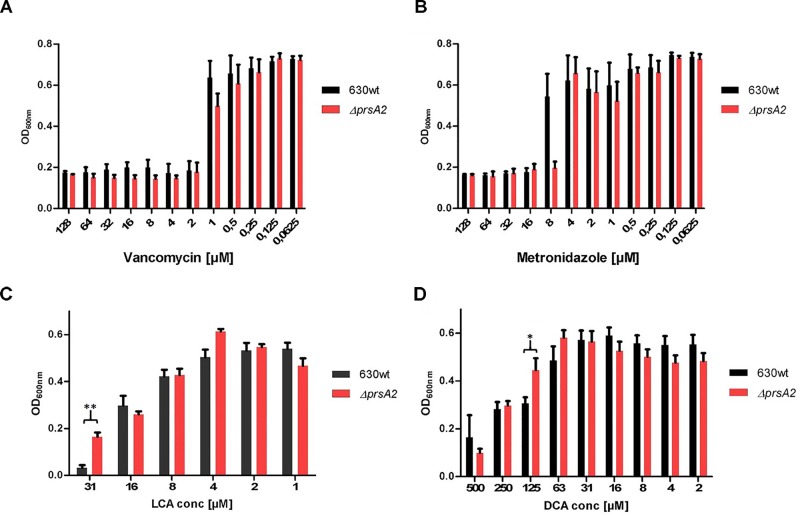
FIGURE 4.
CdPrsA2 confers metronidazole resistance and renders the bacteria sensitive to secondary bile acids. (A) Vancomycin is equally effective against vegetative C. difficile 630Δerm (wild type) and its isogenic ΔprsA2::ClosTron mutant with a minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of ≥ 1 μM. (B) In case of metronidazole the ΔprsA2::ClosTron mutant showed increased sensitivity as the MIC dropped from ≥ 8 μM to ≥4 μM. In the absence of PrsA2 C. difficile can tolerate higher concentrations of the secondary acids (C) litocholic acid (LCA) and (D) deoxycholic acid (DCA) as the MICs for the substances increase from ≥ 16 μM to ≥31 μM, and from ≥63 μM to ≥125 μM, respectively. Shown are the mean and standard deviation of three independent experiments performed in duplicates. Significance was calculated using unpaired two-sided Student’s t-test (∗p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗p ≤ 0.01).