Figure 1.
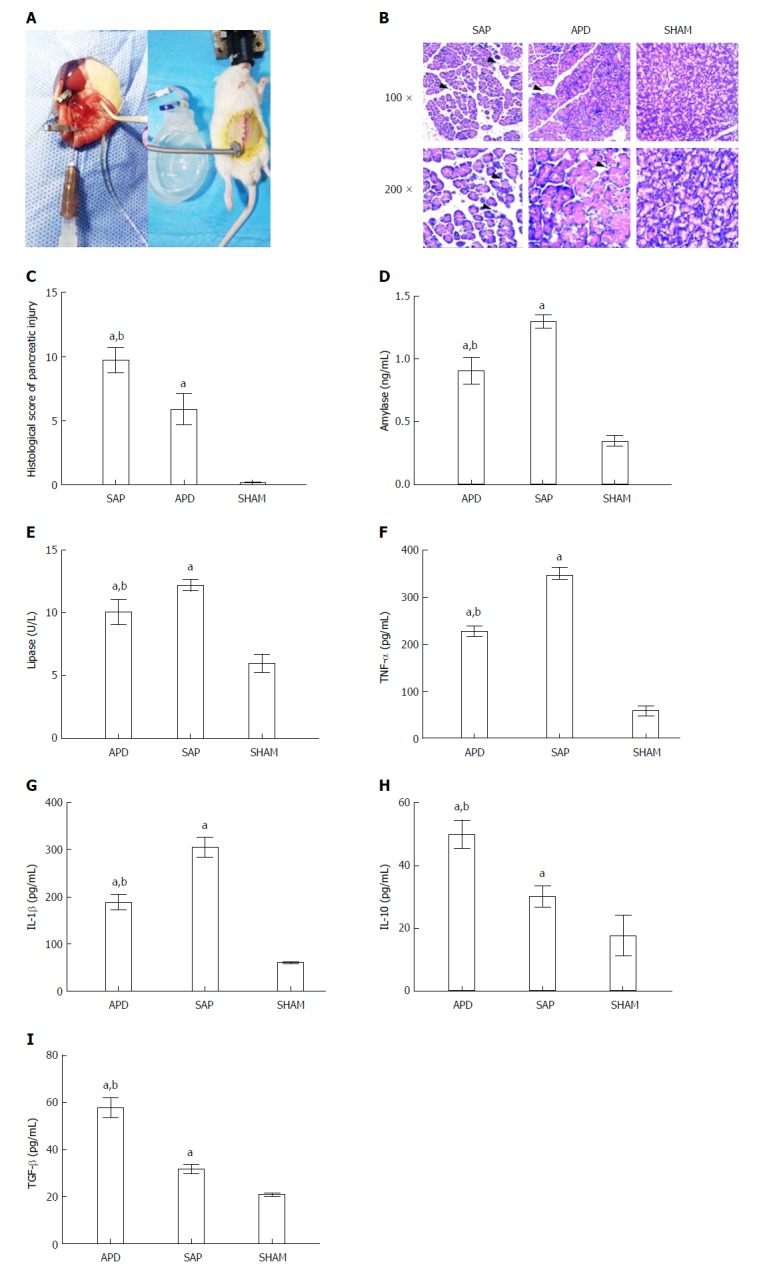
Abdominal paracentesis drainage ameliorates severe acute pancreatitis in a rat model. A: Model establishment. Retrograde injection of Na-taurocholate (left) and a rat after abdominal paracentesis drainage (APD) treatment (right); B and C: Histopathological analysis of the pancreas. Comprehensive disruption of the pancreatic structure with widespread infiltration of leukocytes, acinar cell vacuolization and necrosis was observed in severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) rats; localized leukocyte infiltration and relatively intact acinar structure were observed in APD rats; D-I: Plasma levels of amylase, lipase, tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-10 and transforming growth factor-β, respectively. Data indicate the mean ± SD of six mice (C-I). aP < 0.05 vs sham, bP < 0.05 vs SAP.
