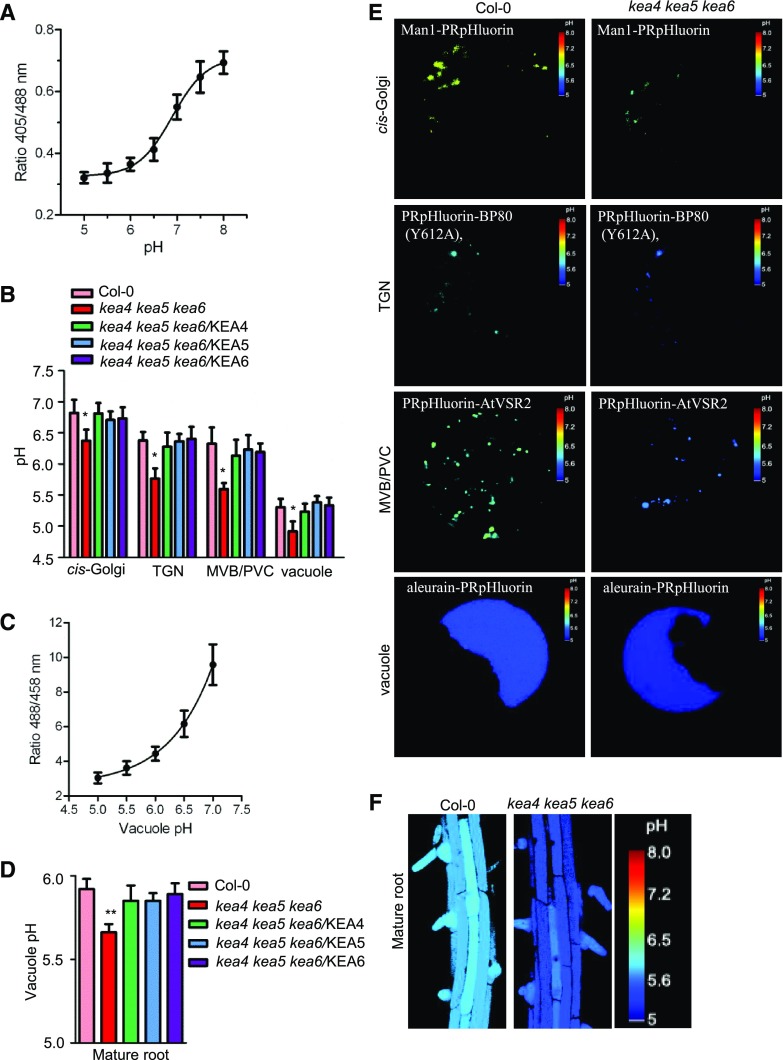
Figure 8.
The kea4 kea5 kea6 mutant has a more acidic pH in the endomembrane compartments. A, In vivo calibration curve of the pH of the cytoplasm. pH was measured using Arabidopsis protoplasts transiently expressing the Golgi-specific Man1-PRpHluorin, TGN-specific PRpHluorin-BP80 (Y612A), PVC/MVB-specific PRpHluorin-AtVSR2, and vacuole-specific aleurain-PRpHluorin. The images were taken with a Leica TCS SP5 laser scanning confocal microscope. The calibration curve was achieved by equilibrating intracellular pH with 25 μm nigericin, 60 mm KCl, and 10 mm MES/HEPES Bis-Tris-propane, pH 5 to 8 (mean ± se; n ≥ 20 protoplasts). B, pH of the Golgi, TGN, PVC/MVB, and vacuole (mean ± se; n ≥ 20 protoplasts). Statistics by Student’s t test are shown: *, P < 0.05. C, In situ calibration curve of the pH of BCECF-AM dye-loaded roots. The calibration was performed by plotting the ratio of emission fluorescence (505–550 nm), obtained when dye-loaded roots were excited with 458 and 488 nm, against the pH of equilibration buffers as described in “Materials and Methods.” Fluorescence images were collected 15 min after roots were incubated in equilibration buffers (mean ± se; n = 10 roots). D, Vacuolar pH of the mature root measured by BCECF-AM (mean ± se; n = 10 roots). Statistics by Student’s t test are shown: **, P < 0.01. E, Representative pseudocolored images for the organellar pH assays. The organelle-specific pHlurions were described in A. F, Ratio images of epidermal cells of the mature root zone in Col-0 and the kea4 kea5 kea6 mutant.