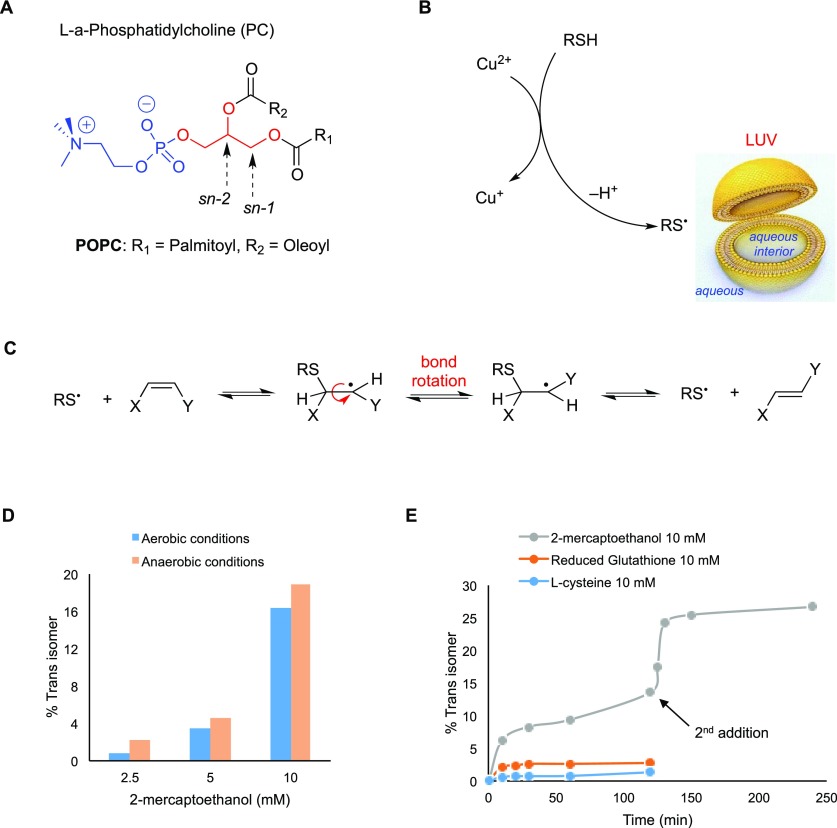
Figure 9.
(A) Molecular structures of l-α-phosphatidylcholine; in the sn-1 and sn-2 positions of the glycerol moiety, the two fatty acid residues are attached, whereas in the sn-3 position, the polar head group is connected. (B) A large unilamellar vesicle (LUV) and the generation of thiyl radicals by reaction of thiol with Cu-TPMA-Phen. (C) Reaction mechanism for the cis–trans isomerization catalyzed by thiyl radicals. (D) Trans isomer (elaidate) formation in POPC vesicles treated with 0.15 mM Cu-TPMA-Phen and different concentrations of 2-mercaptoethanol under aerobic or anaerobic conditions. (E) Trans isomer (elaidate) formation in POPC vesicles treated with 10 mM concentration of different thiols, 0.15 mM Cu-TPMA-Phen, and incubated at 37 °C under aerobic conditions. In the case of 2-mercaptoethanol, after 120 min, another 10 mM thiol was added.