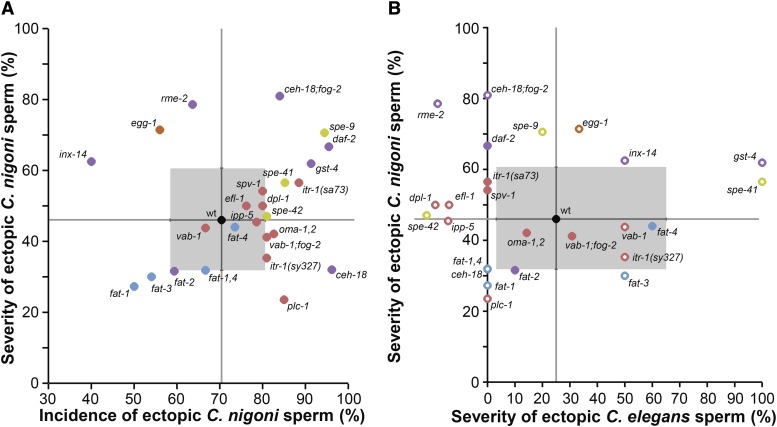
Figure 3.
Severity of ectopic migration of sperm from C. nigoni and C. elegans. (A) The severity of ectopic sperm migration from C. nigoni males is partly decoupled from its incidence, showing no significant correlation across mutant genotypes (Spearman’s ρ= 0.21, df = 24, P = 0.31). Individual mutant strains with concordant influence on both severity and incidence occur in the upper-right and lower-left quadrants of severity × incidence space relative to the wildtype N2 strain values (wt). Mutant strain values in the upper-left and lower-right quadrants relative to wildtype exhibit discordant trends between incidence and severity when faced with heterospecific C. nigoni sperm. (B) The severity of ectopic sperm in C. elegans hermaphrodites exhibits species-specific outcomes for C. nigoni vs. C. elegans males (Spearman’s ρ= 0.16, df = 19, P = 0.48). Gray lines provide reference lines for wildtype values; gray boxes indicate binomial 95% confidence intervals for the wildtype; error bars for mutants not shown for visual clarity. Error bars are larger for severity from C. elegans sperm due to the rarity of individuals that contained any ectopic sperm; mutant strains with <5 individuals observed to have ectopic sperm from C. elegans males are shown with unfilled points (mutants with zero individuals with ectopic sperm shown to the left of the y-axis). Mutant strains are colored to indicate phenotypic effects as in Figure 1 (Supplementary Table S1).