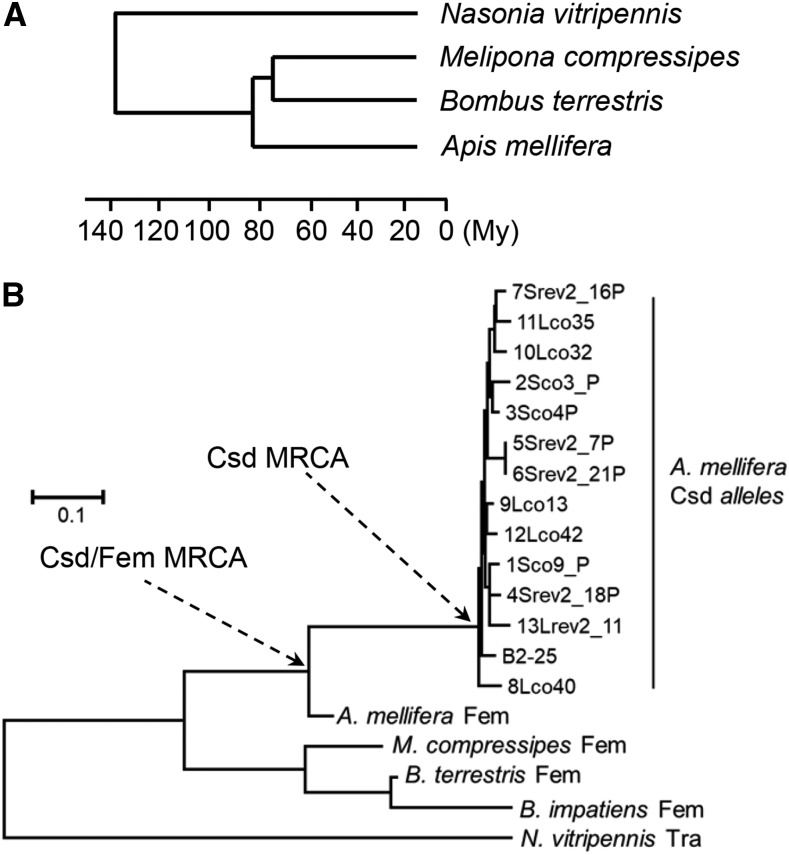
Figure 1.
The evolutionary relationship of the bumble bee and honeybee species (Apis mellifera) and the post duplication divergence of the Fem and Csd proteins in the honeybee lineage (Hasselmann et al. 2008a). A: Time calibrated phylogenetic tree (in millions of years, My) of three bee species and one wasp species (Ramírez et al. 2010; Cardinal and Danforth 2013; Romiguier et al. 2016). B: The evolutionary history of protein sequences of selected bee and wasp species with the divergence of the Fem proteins and Csd alleles in the honeybee (Apis mellifera) lineage. The tree was inferred using the Neighbor-Joining method. Evolutionary distances were computed using the JTT matrix-based method and the modeling of rate variation among sites with a gamma distribution. The units are the number of amino acid substitutions per site. The species were: Apis mellifera, Bombus terrestris, Bombus impatiens, Melipona compressipes, Nasonia vitripennis. The Most Recent Common Ancestor (MRCA) of Csd and Fem proteins and Csd alleles in the honeybee lineage are marked with an arrow.