Fig. 3.
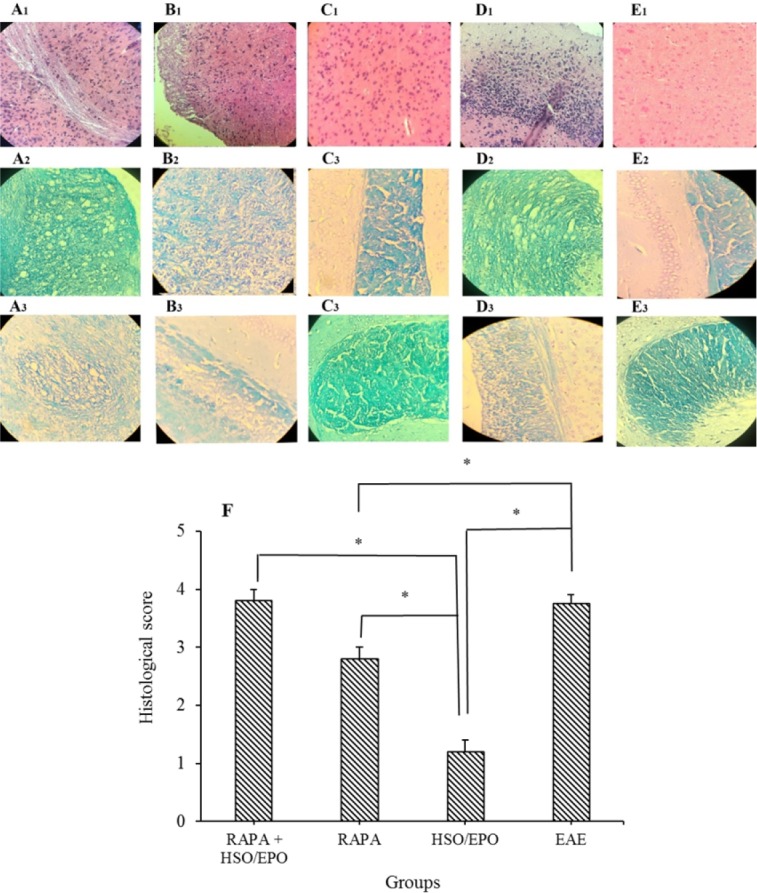
Pathological analysis of brain sections. Group A, RAPA + HSO/EPO-treated mice showed (A1) a large number of inflammatory cells, strings of the non-myelin axon, neuronophagia, (A2) vacuolation, spongy lesions, and (A3) extensive demyelination; group B, rapamycin-treated mice showed (B1) infiltration of inflammatory cells, (B2) spongiotic zones, and (B3) demyelination; group C, HSO/EPO-treated mice showed (C1), a few inflammatory cells and (C2,3) without spongy lesions and demyelination; group D, EAE mice showed (D1) extensive focal inflammatory cells, (D2) extensive vacuolation, zones of spongy degeneration, and (D3) demyelination; group E1-3, the section of the brain of naive mice exhibited no clinical signs. The first row was stained with H&E, the second and third rows were stained with LFB; F, histological score: 0 = no pathology, 1 = no tissue damage but minor inflammation, 2 = modest inflammation, prime tissue damage and demyelination, 3 = moderate tissue damage (demyelination, neuronal loss, tissue damage, cell death, neuronal vacuolation, and neuronophagia), 4 = necrosis (loss of all tissue elements entirely with associated cellular remains). Data presented as mean ± SEM. *P value ≤ 0.05 is significant. EAE, experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; HSO/EPO, hemp seed oil/evening primrose oil; RAPA, rapamycin; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; LFB, luxol fast blue.
