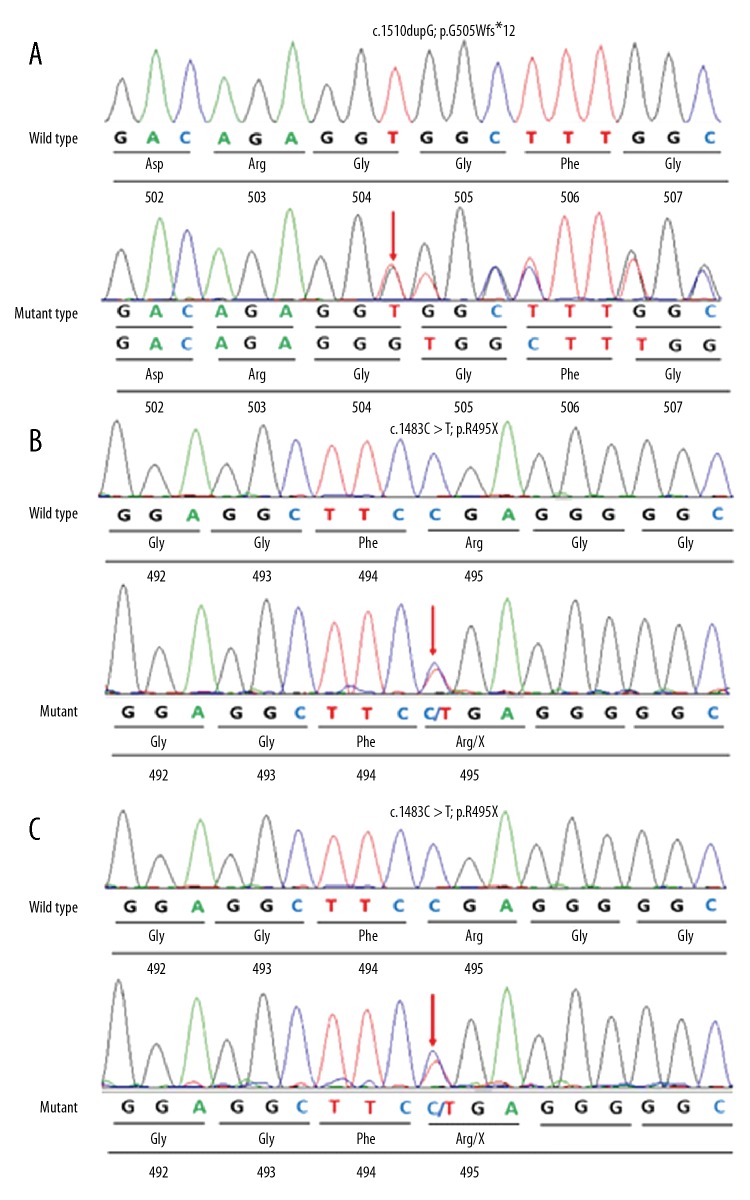
Figure 4.
Sequencing chromatograms of the p.G505Wfs*12 mutation of Patient One, and p.R495X mutation of Patient Two and his mother, Patient Three. (A) Sequencing chromatograms of the p.G505Wfs*12 mutation of Patient One. The arrow shows the position of a G duplication at nucleotide 1510 (c.1510dupG), and creates a premature stop codon (p.G505Wfs*12), which is supposed to produce a C-terminally truncated fused in sarcoma protein (the resulting protein would be 515 amino acids long). (B) Sequencing chromatograms of the p.R495X mutation of Patient Two. The arrow shows the position of a C-to-T transversion at nucleotide 1483 (c.1483C>T) that leads to production of a C-terminally truncated fused in sarcoma protein. (C) Sequencing chromatograms of the p.R495X mutation of Patient Three. The arrow shows the position of a C-to-T transversion at nucleotide 1483 (c.1483C>T), which leads to production of a C-terminally truncated fused in sarcoma protein.