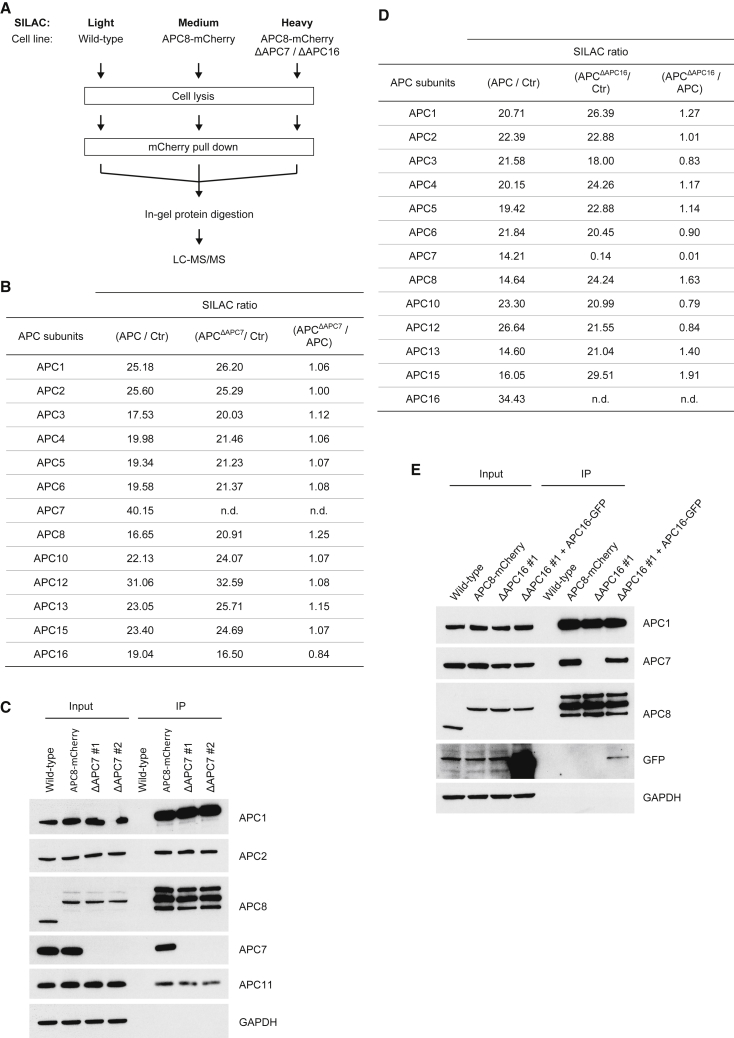
Figure 1.
APC16 Is Required for Assembly of APC7 into APC/C
(A) Experimental setup for MS-based analysis of APC/C composition. APC8-mCherry-expressing wild-type cells were labeled with medium SILAC, and ΔAPC7 or ΔAPC16 cells were labeled with heavy SILAC. APC/C was purified using mCherry affinity beads, and as a control, a mock pull-down was performed from light SILAC-labeled cells.
(B) SILAC ratios for APC/C subunits enriched from APC8-mCherry wild-type and APC8-mCherry ΔAPC7 cells. APC/C was purified with mCherry pull-downs from wild-type (medium SILAC) and ΔAPC7 cells (heavy SILAC) and analyzed by MS. Mock pull-down from wild-type HCT116 cells served as a control (light SILAC). The table shows combined SILAC ratios for APC/C subunits detected in three technical replicates (n.d., not determined).
(C) Analysis of APC/C composition in ΔAPC7 cells. APC/C was purified via APC8-mCherry pull-downs from APC8-mCherry and APC8-mCherry ΔAPC7 cells (from two independent ΔAPC7 clonal cell lines) and subsequently analyzed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies. Wild-type cells were used as a control for unspecific binding to the affinity beads. GAPDH levels were analyzed to verify equal amounts of input for the different cell lines.
(D) SILAC ratios for APC/C subunits enriched from APC8-mCherry and APC8-mCherry ΔAPC16 cells. The analysis was performed as described in (B).
(E) Immunoblot analysis of APC/C composition in ΔAPC16 cells with the indicated antibodies. APC/C was purified via APC8-mCherry pull-downs from APC8-mCherry cells and from APC8-mCherry ΔAPC16 cells. The indicated samples were transiently transfected with APC16-EGFP 32 hr prior to APC/C pull-down. Wild-type cells were used as a control for unspecific binding to the affinity beads.
See also Figure S1.