Figure 1.
Determining Somatic Mutations in Hematopoietic Progenitors
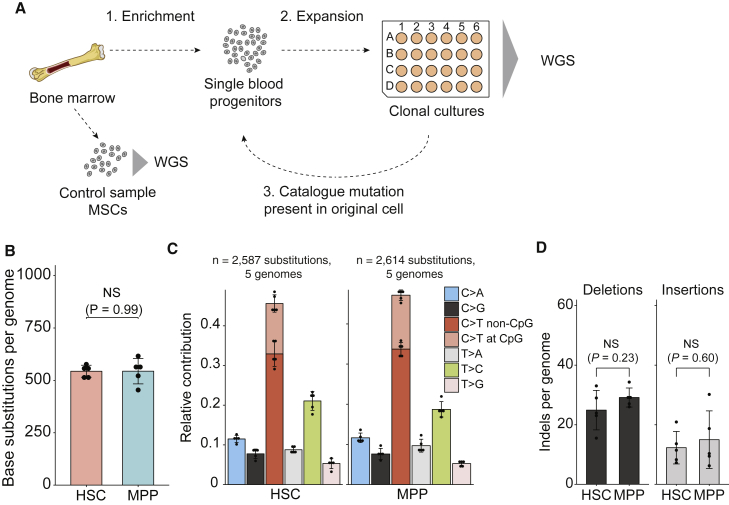
(A) Schematic overview of experimental setup to catalog somatic mutations in single human blood progenitors. MSCs, mesenchymal stem cells; WGS, whole-genome sequencing.
(B) Average number of base substitutions in HSCs and MPPs (extrapolated to the whole autosomal genome) of the donor A. Error bars indicate SD. Each data point represents a single HSC or MPP clone. The p value indicates no statistical difference (NS) between the number of base substitutions in HSCs and MPPs (two-sided t test).
(C) Relative contribution of the indicated mutation types to the base substitution spectra in HSCs and MPPs. Error bars indicate SD. Each data point represents a single HSC or MPP clone.
(D) Average number of indels in HSCs and MPPs (extrapolated to the whole autosomal genome) of the donor A. Error bars indicate SD. Each data point represents a single HSC or MPP clone. The p values indicate no statistical difference (NS) between the number of indels in HSCs and MPPs (two-sided t test).