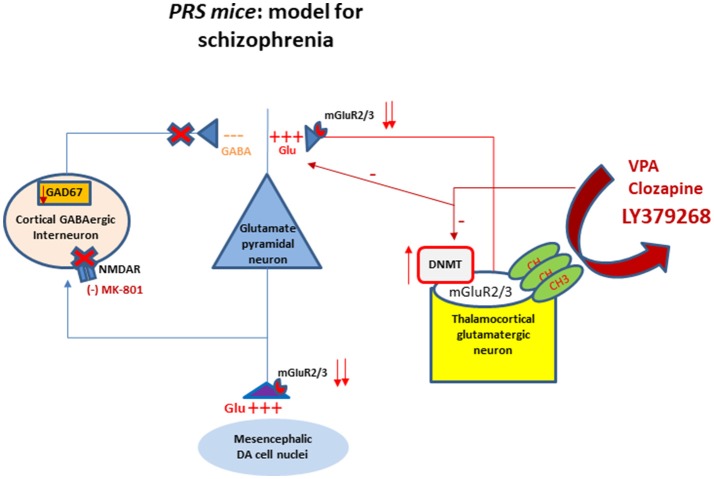
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the interactions between GABAergic and glutamatergic neurotransmission in cortical-limbic structures of PRS mice. The cartoon shows altered DNA promoter hypermethylation (increase in DNMT) occurring at the mGlu2/3 receptors gene promoter and their decreased expression at presynaptic level of thalamocortical glutamatergic neurons. The downregulation of mGlu2/3 receptors at the axon terminal of thalamocortical glutamatergic neurons results in the hyperactivation of glutamatergic pyramidal neurons. This activation is facilitated by a decrease of GABAergic feedback inhibition on pyramidal neurons. The hypofunction of GABAergic interneurons is mediated by a downregulation of NMDA receptor function as suggested by the behavioral hypersensitivity to small doses of NMDA receptor blocker MK-801 (Matrisciano et al., 2013). The same fibers project to subcortical areas causing an excessive firing and dopamine release. The cartoon shows also the mGlu2/3 receptors at presynaptic level of the thalamocortical fibers as potential target for pharmacological interventions such as the mGlu2/3 receptor agonist LY379268, valproate and clozapine to restore the normal balance between GABA and glutamate through epigenetic mechanisms. DA, dopaminergic; DNMT, DNA methytransferase; NMDA, N-methyl-D-aspartate; CH3, methyl group.