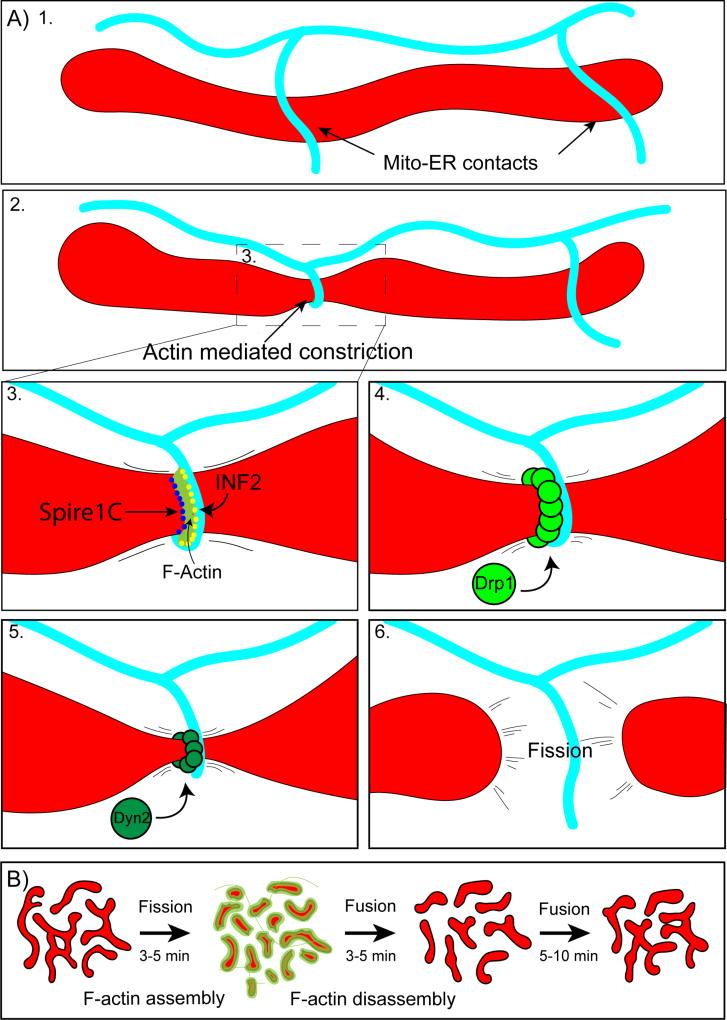
Figure 2.
A) INF2/Spire1C mediated mitochondrial fission. 1. Mitochondria make frequent contacts with endoplasmic reticulum tubules (Mito-ER contacts). 2. A subset of Mito-ER contact sites mark prospective sites of mitochondrial fission. At these sites, ER tubules wrap around mitochondria generating a constriction event. 3. ER constriction around mitochondria is driven by actin polymerization by INF2 on the ER and Spire1C on mitochondria. 4. Once mitochondria undergo constriction, Drp1 forms rings at the constriction site which pinch down the organelle, decreasing the cross sectional diameter. 5. Next, Dyn2 assembles and completes the process of mitochondrial fission (6). B. Arp2/3 mediated mitochondrial fission. Actin transiently assembles on locally hyperfused regions of the mitochondrial network. Actin assembly promotes rapid fission over 3–5 minutes. Mitochondria then fuse back together and the process repeats.