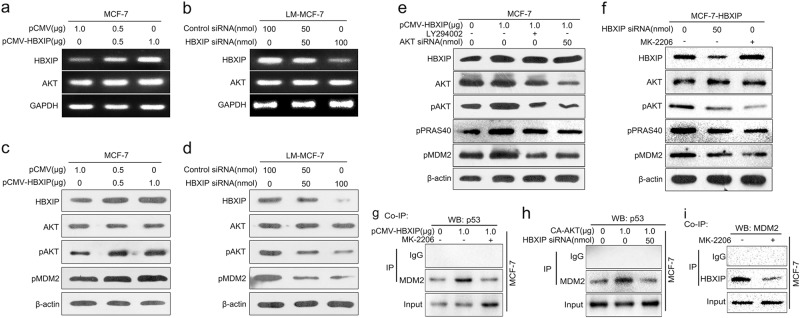
Fig. 4.
HBXIP enhances the interaction between p53 and MDM2 via promoting the phosphorylation of MDM2 mediated by AKT and binding to pMDM2. a, b The mRNA levels of HBXIP and AKT were detected by RT-PCR in MCF-7 and LM-MCF-7 cells. c, d The levels of HBXIP, total AKT, pAKT, and pMDM2 were examined by Western blot analysis in MCF-7 cells transfected with pCMV-HBXIP (or pCMV) and LM-MCF-7 cells transfected with HBXIP siRNA (or Control siRNA). e Effects of LY294002 (a PI3K inhibitor) or AKT siRNA on the levels of total AKT, pAKT, phosphorylated PRAS40 (Proline-rich AKT substrate 40 kDa) and pMDM2 were examined by Western blot analysis in MCF-7 cells when HBXIP was overexpressed. f Effects of MK-2206 (an AKT inhibitor) or HBXIP siRNA on the levels of total AKT, pAKT, pPRAS40, and pMDM2 were examined by Western blot analysis in MCF-7-HBXIP cells. g, h The interaction between MDM2 and p53 was determined by co-IP assay in MCF-7 cells treated with pCMV-HBXIP/MK-2206 or CA-AKT/HBXIP siRNA. i The interaction between HBXIP and MDM2 was detected by co-IP assay in MCF-7 cells treated with MK-2206. Each experiment was repeated at least three times