Figure 1.
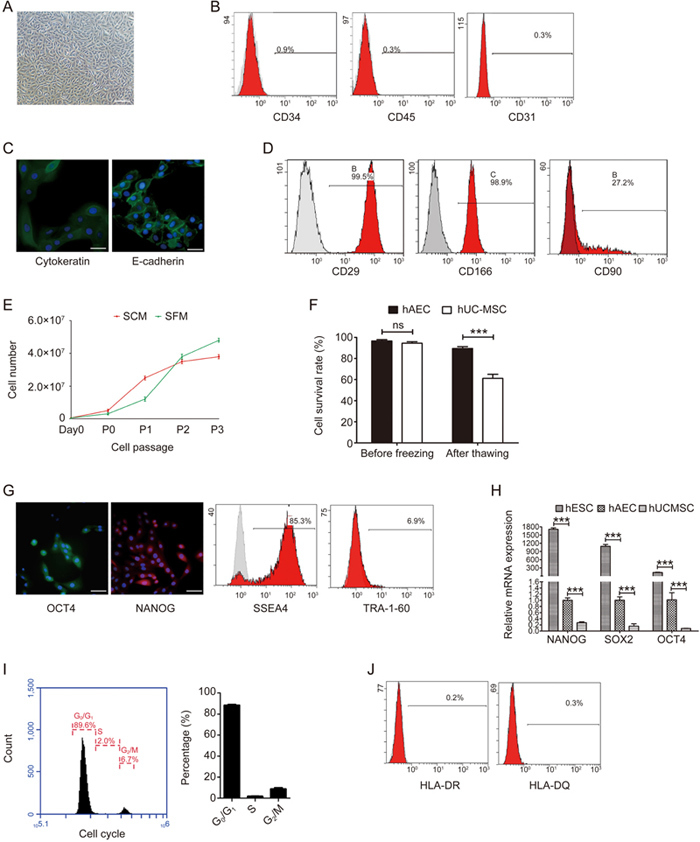
The biological features of hAECs in the serum-free system. (A) Representative light microphotograph of hAECs isolated in the serum-free system; scale bar=200 μm. (B) Flow cytometry detection of the blood cell markers CD45 and CD34 and the endothelial cell marker CD31 in the isolated hAECs. (C) Immunofluorescence microscopy of the epithelium markers pan-cytokeratin (green) and E-cadherin (green) in hAECs. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue); scale bar=50 μm. (D) Flow cytometry detection of CD29, CD166 and CD 90 in the isolated hAECs. (E) Growth curves of hAECs in serum and serum-free systems. (F) 5×106/mL P1 hAECs or hMSCs were cryopreserved using CELLBANKER serum-free cryopreservation media and thawed after 30 d. The survival rates of hMSCs and hAECs were determined by trypan blue exclusion. (G) Immunofluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry detection of the pluripotent markers OCT4 (green), NANOG (red), SSEA4 and TRA-1-60 in hAECs. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue); scale bar=50 μm. (H) Quantitative real-time PCR assessment of the expression of Nanog, Sox2 and Oct4 in hESCs, hAECs and hMSCs. (I) Representative histogram and statistics of the cell cycle phase distribution of hAECs. (J) Flow cytometry detection of MHC class II markers HLA-DR and HLA-DQ in hAECs.
