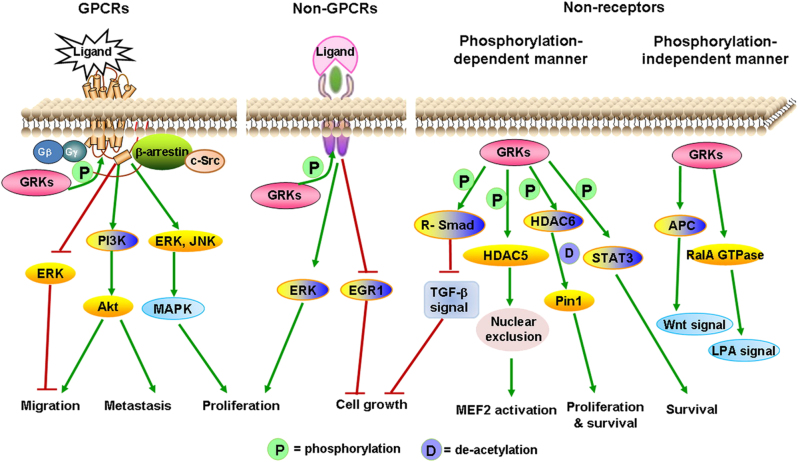
Fig. 1.
Function and GRKs-mediated signal pathways. GRKs phosphorylate agonist-activated GPCRs, which allows the recruitment of β-arrestins, thereby terminating or inducing the GPCRs-mediated signal transduction pathways. In addition, GRKs can also interact with non-GPCRs or non-receptor substrates, including participating in signal transduction in both a phosphorylated manner and non-phosphorylated manner. This associated signal regulation by GRKs promotes or inhibits different cellular functions, such as cell growth, proliferation, migration, metastasis, and survival