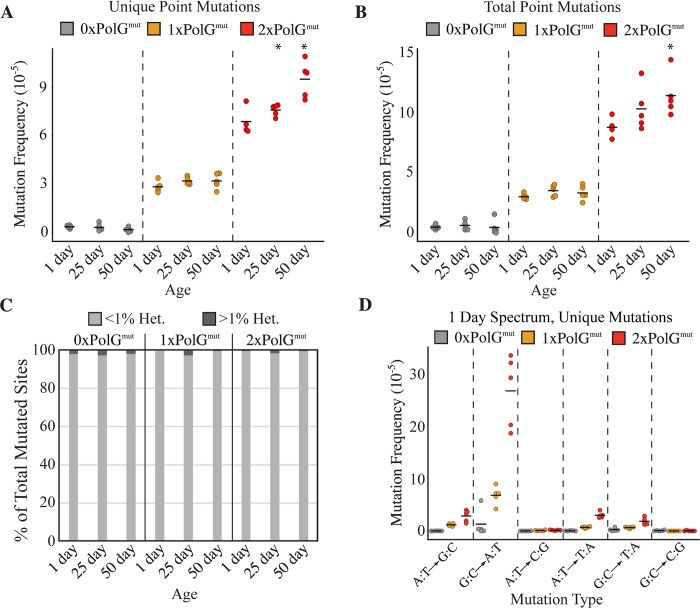
Fig 2. Transgenic expression of an exonuclease-deficient PolG results in a dose-dependent increase in mutation frequency.
The frequencies of base substitution mutations were quantified in 1-day-old, 25-day-old, and 50-day-old flies of the given genotype using DS. (A) The mutation load of unique mutations, representing each unique mutation counted once, thus reflecting the de novo somatic mutation frequency. (B) The frequency of total mutations. (C) The percentage of mutated sites at sub-clonal levels (<1% heteroplasmy) and clonally expanded mutations (≥1% heteroplasmy) in flies of the indicated age and genotype. (D) The frequency of unique mutations of each type of base substitution mutation is indicated in 1-day-old flies of the indicated genotypes. N = 5 per genotype per time point. Horizontal bars in panels A, B, and D represent the mean frequency of the indicated group. *p < 0.05 compared to 1-day-old flies of the same genotype by Wilcoxon rank-sum test. 1x and 2xPolGmut flies displayed significantly elevated mutation frequencies compared to age-matched control 0xPolGmut flies at all time points (p<0.05 by Wilcoxon rank-sum test).