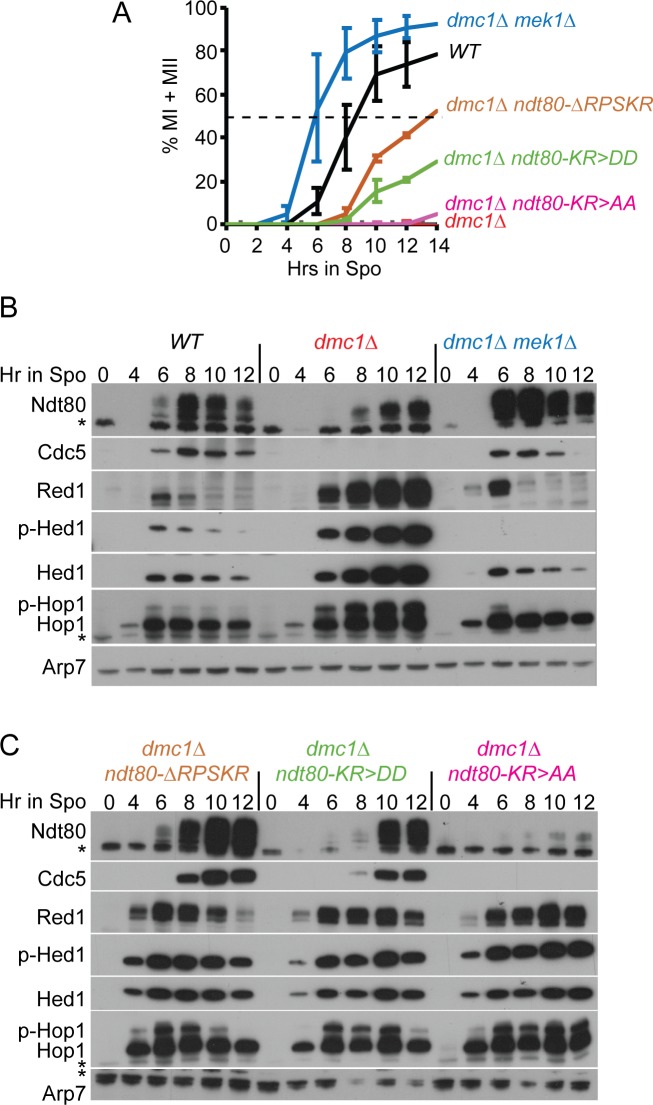
Fig 3. Mek1 interaction-defective ndt80 mutants bypass the dmc1Δ meiotic recombination checkpoint arrest.
WT (NH2081::pHL82), dmc1Δ, (NH2402::pHL82), dmc1Δ mek1Δ (NH749), dmc1Δ ndt80-ΔRPKSR (NH2402::pNH3172), dmc1Δ ndt80-KR>AA (NH2402::pHL8-KR>AA2) and dmc1Δ ndt80-KR>DD (NH2402::pHL8-KR>DD2) were transferred to Spo medium at 30°C and cells analyzed at the indicated timepoints. (A) Meiotic progression. The percent of cells completing either MI or MII was determined using fluorescence microscopy of DAPI-stained nuclei. Two hundred cells were counted per timepoint. The average values of two experiments were plotted with error bars indicating the range. (B) Immunoblot analysis of extracts from WT, dmc1Δ and dmc1Δ mek1Δ diploids taken at the indicated timepoints from one of the timecourses shown in A. (C) Immunoblot analysis of extracts from dmc1Δ ndt80-ΔRPSKR, dmc1Δ ndt80-KR>DD and dmc1Δ ndt80-KR>AA diploids taken at the indicated timepoints from one of the timecourses shown in A. Phospho-Hop1 (p-Hop1) is an indirect indicator of DSBs, while phospho-Hed1 T40 (p-Hed1) is a marker for Mek1 kinase activity. The asterisks indicate non-specific bands. Arp7 was used as a loading control.