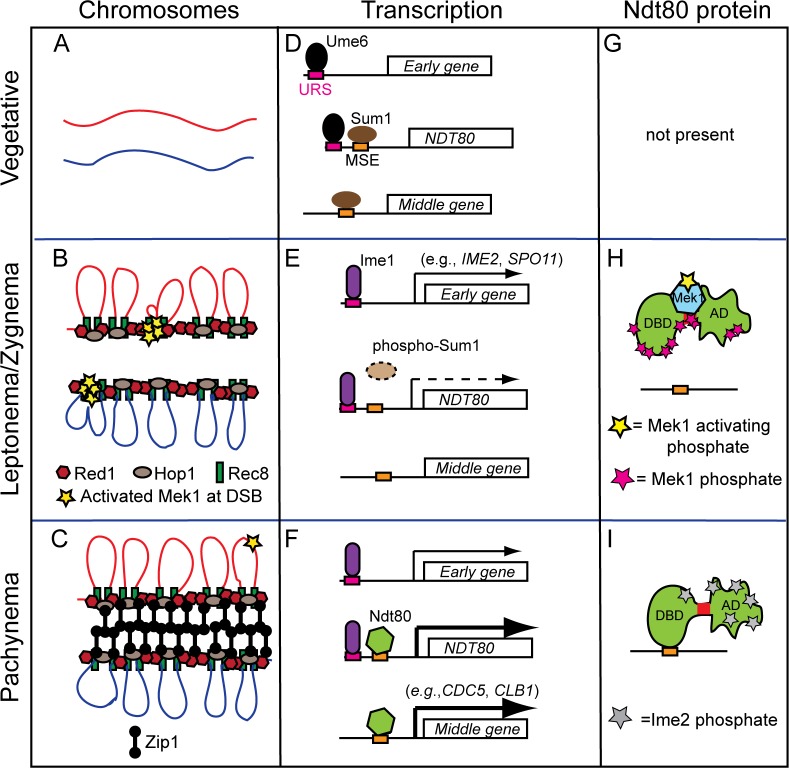
Fig 7. Model for regulation of Ndt80 activity by Mek1.
The status of chromosomes, gene transcription and Ndt80 protein at different cell states is shown in three different columns as indicated. (A) Unreplicated pair of homologous chromosomes. (B) Entry into meiosis results in expression of early genes and the condensation of sister chromatids onto axial cores formed of Hop1, Red1 and Rec8 (only one chromatid from each homolog is shown). Hotspot sequences tethered to the axes are cleaved by Spo11, resulting in the recruitment and activation of Mek1 at the axis (yellow stars). (C) Repair of DSBs via the ZMM pathway promotes double Holliday junction formation and synapsis by the insertion of Zip1 between the axial elements to form the SC. Low levels of DSBs continue to occur until the SC is disassembled. (D) In vegetative cells, meiotic early genes and NDT80 are repressed by the Ume6/Isw2/Sin3-Rpd3 repression complex bound to URS1 sites in their promoters. The Sum1 repressor is bound at MSE sites in the promoters of NDT80 and middle genes (for simplicity, only one URS1 and one MSE are shown for the NDT80 promoter). (E) Transfer to sporulation medium results in the replacement of the Ume6 repressor with the Ime1 transcriptional activator at URS1 elements, resulting in early gene transcription (indicated by a solid arrow). Ime1-driven transcription of NDT80 is delayed (indicated by dashed arrow) until the Ime2 kinase phosphorylates Sum1, thereby allowing its removal from MSEs. (F) Active Ndt80 binds to MSEs in its own promoter to initiate the positive feedback loop, as well as the promoters of middle genes. (G) The NDT80 gene is not transcribed in vegetative cells so the protein is absent. (H) The low level of Ndt80 protein produced by Ime1 is bound by activated Mek1 and phosphorylated, thereby preventing it from binding to DNA. (I) As chromosomes synapse, the bulk of Mek1 is removed and Mek1 activity decreases. The loss of Mek1 inhibitory phosphorylation, as well as the addition of Ime2 activating phosphates, allows Ndt80 to bind to MSEs and activate transcription.