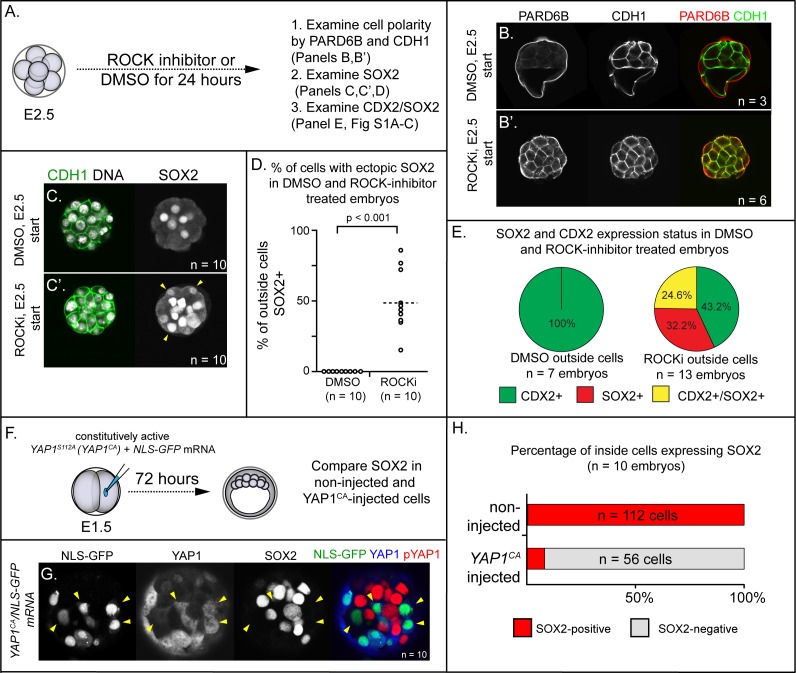
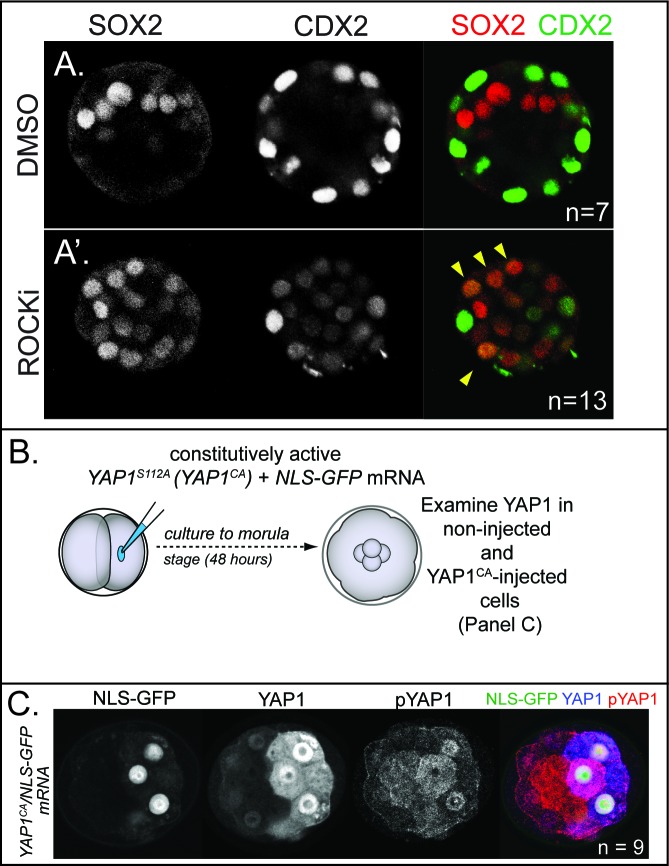
Figure 1. ROCK1/2 and nuclear YAP1 repress expression of SOX2.
(A) Experimental design: embryos were collected at E2.5 and treated with ROCK inhibitor Y-27632 (ROCKi) or DMSO (control) for 24 hr. (B–B’) Confocal images of apical (PARD6B) and basolateral (CDH1) membrane components in control and ROCKi-treated embryos. As expected, PARD6B and CDH1 are mislocalized to the entire cell membrane of all cells in ROCKi-treated embryos, demonstrating effective ROCK inhibition (n = number of embryos examined). (C–C’) In control embryos, SOX2 is detected only in inside cells, while in ROCKi-treated embryos, SOX2 is detected in inside and outside cells (arrowheads, outside cells; n = embryos). (D) Quantification of ectopic SOX2 detected in outside cells of control and ROCKi-treated embryos (p, student’s t-test, n = embryos). (E) SOX2 and CDX2 staining in outside cells of control and ROCKi-treated embryos. ROCK-inhibitor treatment leads to outside cells with mixed lineage marker expression (CDX2+/SOX2+). (F) Experimental design: embryos were collected at E1.5 and one of two blastomeres injected with mRNAs encoding YAP1CA and GFP. Embryos were cultured for 72 hr, fixed, and then analyzed by immunofluorescence and confocal microscopy. (G) SOX2 is detected non-injected inside cells. SOX2 is not detected in YAP1CA-overexpressing inside cells (arrowheads), n = embryos. (H) Across multiple embryos, all non-injected inside cells express SOX2, whereas the vast majority of YAP1CA-injected inside cells fail to express SOX2.