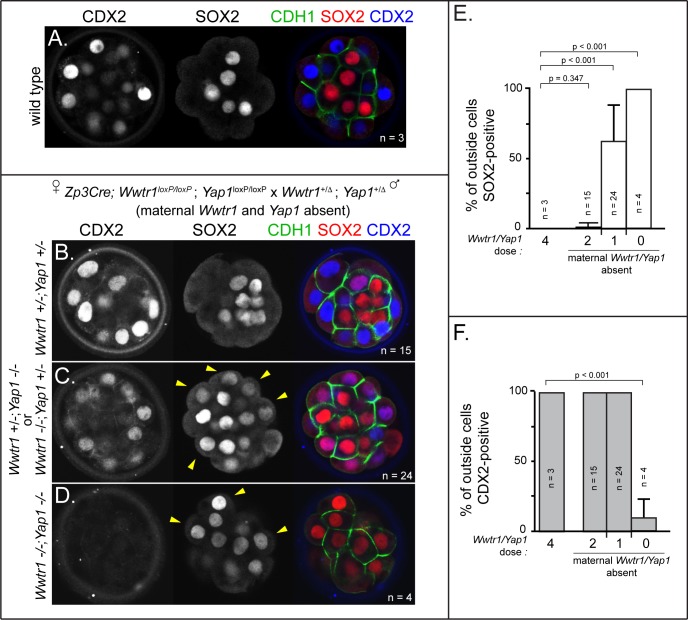
Figure 5. Wwtr1 and Yap1 are required to repress SOX2 expression in outside cells.
(A) CDX2 and SOX2 in wild type embryos at E3.25 (16–32 cell stages). CDX2 staining is more intense in outside cells than inside cells and SOX2 staining is specific to inside cells (n = embryos). (B) Embryos lacking maternal Wwtr1 and Yap1 with and heterozygous for Wwtr1 and Yap1 (which we consider to have 2 doses of WWTR1/YAP1) exhibit normal CDX2 and SOX2 expression (n = embryos). (C) Embryos lacking maternal Wwtr1 and Yap1 and heterozygous for either Wwtr1 or Yap1 (1 dose of WWTR1/YAP1) exhibit a high degree of ectopic SOX2 in outside cells (arrowheads), but continue to express CDX2, although the levels appear reduced (n = embryos). (D) Embryos lacking maternal and zygotic Wwtr1 and Yap1 (0 doses of WWTR1/YAP1) have the most severe phenotype, with a high degree of ectopic SOX2 in outside cells (arrowheads) and little or no detectable CDX2 (n = embryos). (E) Quantification of the percentage of outside cells in which ectopic SOX2 is detected in the presence of decreasing dose of Wwtr1 and Yap1 (t = student’s t-test, n = embryos). (F) Quantification of the percentage of outside cells in which CDX2 is detected in the presence of decreasing dose of Wwtr1 and Yap1 (t = student’s t-test, n = embryos).