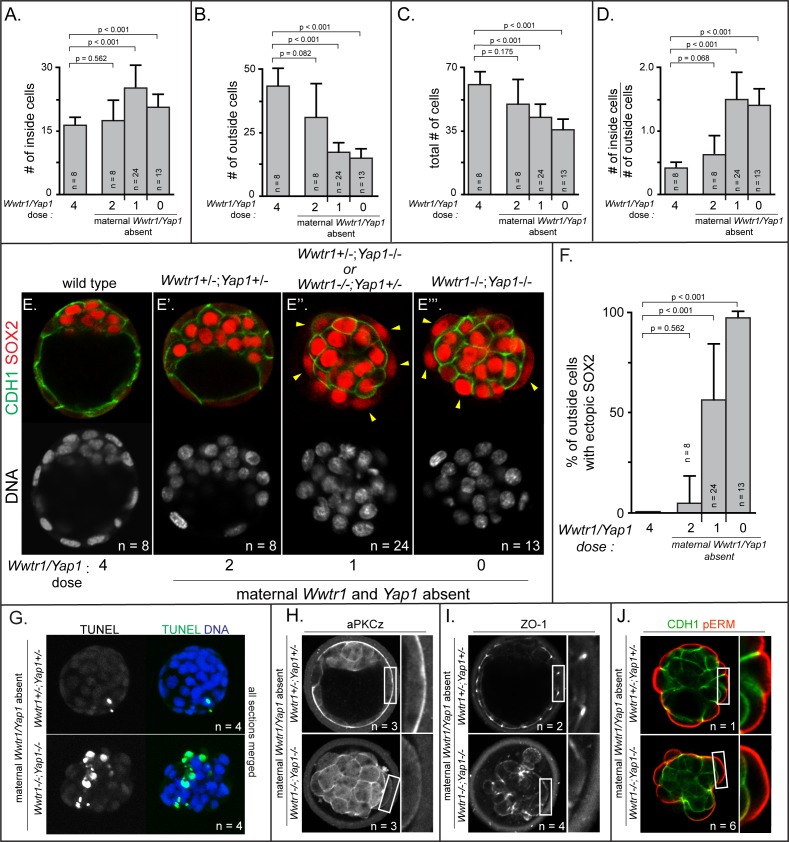
Figure 6. Positioning and epithelialization defects in embryos with Wwtr1 and Yap1 null alleles (A) Quantification of the average number of inside cells per embryo with decreasing dose of Wwtr1 and Yap1.
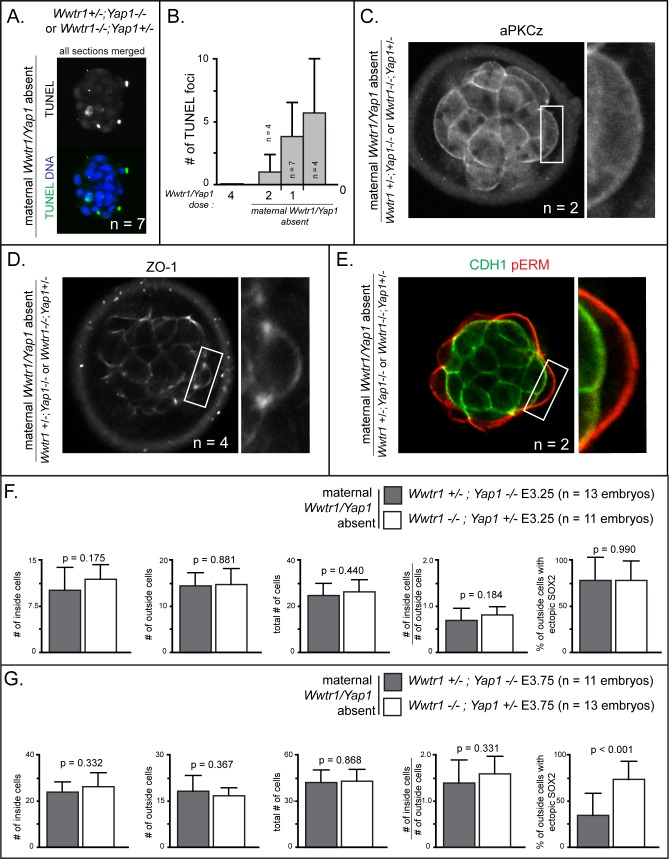
The number of inside cells increases as the dose of wild type Wwtr1 and Yap1 alleles is reduced (p, student’s t-test, n = embryos). (B) Quantification of the average number of outside cells per embryo with decreasing dose of Wwtr1 and Yap1. The number of outside cells decreases as the dose of wild type Wwtr1 and Yap1 alleles is reduced (p, student’s t-test, n = embryos). (C) Quantification of the average number of total cells per embryos with decreasing dose of wild type zygotic Wwtr1 and Yap1. The number of total cells decreases as the dose of wild type Wwtr1 and Yap1 is reduced (p, student’s t-test, n = embryos). (D) Quantification of the average ratio of inside to outside cells per embryo with decreasing dose of Wwtr1 and Yap1. The ratio of inside to outside cells increases as the dose of wild type Wwtr1 and Yap1 is reduced (p, student’s t-test, n = embryos). (E) Wild type embryos at E3.75 exhibit inner cell mass-specific expression of SOX2 (n = embryos). (E’) E3.75 embryos lacking maternal Wwtr1 and Yap1 and heterozygous for zygotic Wwtr1 and Yap1 cavitate and repress Sox2 in outside cells, leading to inner cell mass-specific expression of SOX2 similar to wild type embryos (n = embryos). (E’’) Embryos lacking maternal Wwtr1 and Yap1 but with only one wild type allele of Wwtr1 or Yap1 fail to cavitate and repress Sox2 in outside cells, leading to ectopic SOX2 in outside cells (arrowheads, n = embryos). (E’’’) Embryos lacking maternal and zygotic Wwtr1 and Yap1 fail to cavitate and repress Sox2 in outside cells, leading to ectopic SOX2 in outside cells (arrowheads, n = embryos). (F) Quantification of ectopic SOX2 detected in embryos such as those shown in panels E-E’’’. The percentage of outside cells with ectopic SOX2 increases as the dose of wild type Wwtr1 and Yap1 alleles is reduced (p, student’s t-test, n = embryos). (G) TUNEL analysis of embryos lacking maternal Wwtr1 and Yap1 heterozygous for zygotic Wwtr1 and Yap1 or lacking maternal and zygotic Wwtr1 and Yap1. Extensive TUNEL staining is observed in embryos lacking maternal and zygotic Wwtr1 and Yap1 indicative of cell death. Max projections of all confocal sections from a single embryo are shown (n = embryos). (H) aPKCz staining in embryos lacking maternal Wwtr1 and Yap1, either heterozygous for zygotic Wwtr1 and Yap1 or with no zygotic Wwtr1 and Yap1. aPKC is not localized to the apical membrane of embryos with no zygotic Wwtr1 and Yap1 (n = embryos). (I) ZO-1 staining in embryos lacking maternal Wwtr1 and Yap1, either heterozygous for zygotic Wwtr1 and Yap1 or with no zygotic Wwtr1 and Yap1. ZO-1 is disorganized in embryos with no zygotic Wwtr1 and Yap1, suggesting that formation of a mature epithelium depends on Wwtr1 and Yap1 (n = embryos). (J) pERM and CDH1 staining in embryos lacking maternal Wwtr1 and Yap1, either heterozygous for zygotic Wwtr1 and Yap1 or with no zygotic Wwtr1 and Yap1. pERM is localized to apical membranes and CDH1 to basolateral membranes regardless of the dose of wild type Wwtr1 and Yap1 alleles (n = embryos).