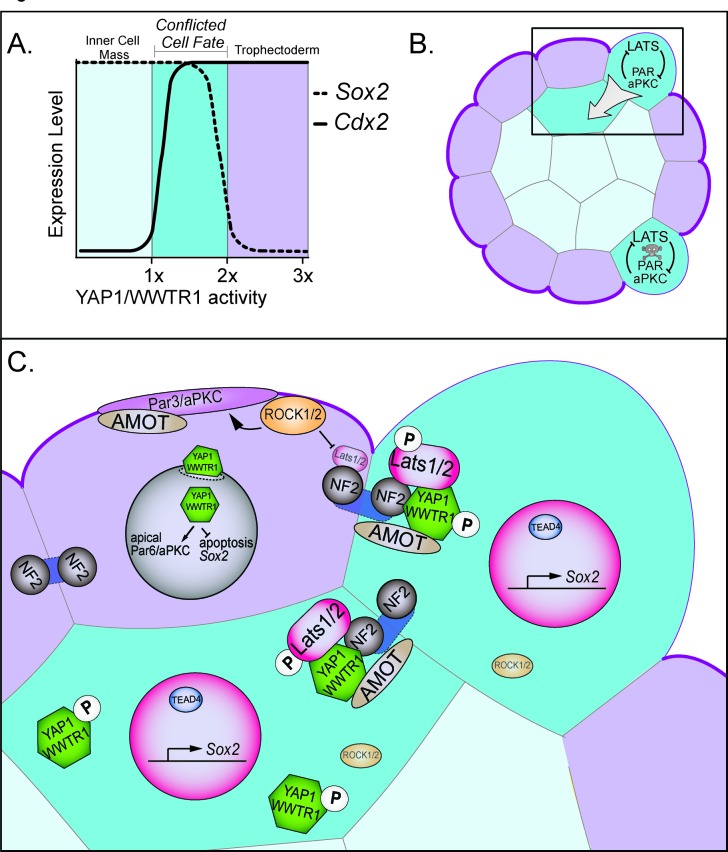
Figure 7. Resolution of cell fate conflicts in the preimplantation mouse embryo.
(A) The expression of Sox2 and Cdx2 is differentially sensitive to YAP1/WWTR1 activity, leading to co-expression of both lineage markers in cells when YAP1/WWTR1 activity levels are intermediate. (B) During division from the 16 to the 32-cell stage, cells that inherit the apical membrane repress HIPPO signaling and maintain an outside position. However, cells that inherit a smaller portion of the apical membrane would initially elevate their HIPPO signaling. We propose that elevated HIPPO then feeds back onto polarity by further antagonizing PAR-aPKC complex formation, leading to a snowball effect on repression of Sox2 expression, and thus ensuring that SOX2 is never detected in outside cells because these cells are rapidly internalized or apoptosed. (C) A closeup of the boxed region in panel B. In most outside cells, low LATS2 activity enables high levels of YAP1/WWTR1 activity, which repress Sox2 and apoptosis and promote Cdx2 expression and apical localization of aPKC and PARD6B, which in turn repress the HIPPO pathway. In rare outside cells, LATS2 activity becomes elevated, leading to lower activity of YAP1/WWTR1, which then leads these cells to become internalized or to undergo apoptosis.