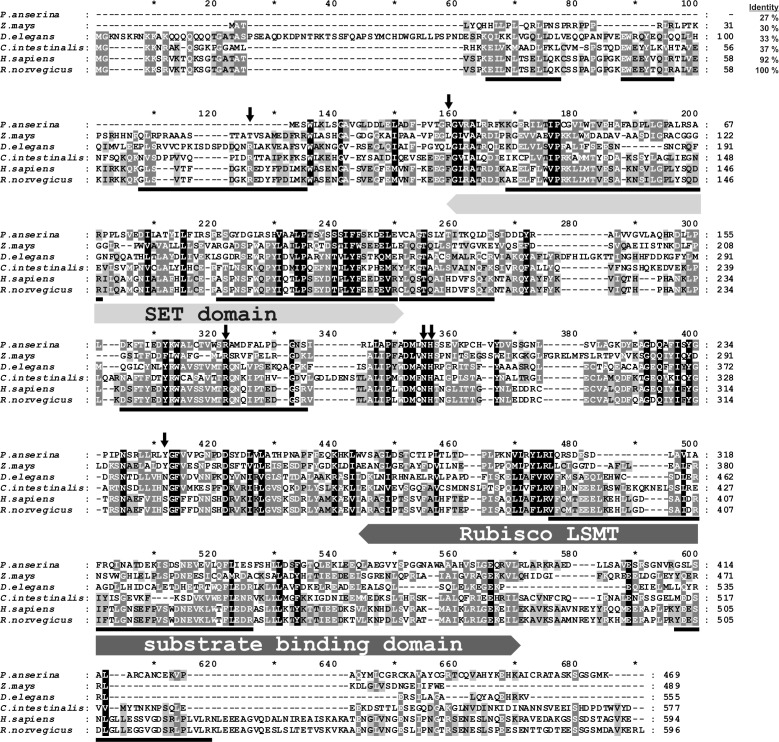
Figure 2. Amino-acid sequence alignment of the rat SETD3 protein with its orthologs.
Sequences of rat (Rattus norvegicus, XP_002726820.2), human (Homo sapiens, NP_115609.2), Ciona intestinalis (C. intestinalis, XP_002131202.1), Drosophila elegans (D. elegans, XP_017114801.1), Podospora anserina (P. anserina, CDP29262.1) and Zea mays (Z. mays, NP_001168589.1) protein were obtained from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Protein database. Both the rat and the human sequences have been confirmed by PCR amplification of the cDNA and DNA sequencing. The percentage of amino-acid identities with the rat SETD3 protein is given in the top right corner of the figure. The conserved protein substrate-binding domains (SET and Rubisco large subunit methyltransferase (LSMT) substrate binding) are labeled above the alignment, while amino-acid residues that interact with S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) are indicated by arrows, as inferred from the crystal structure of the human SETD3 enzyme (PDB 3SMT). The peptides identified by mass spectrometry in the protein purified from rat leg muscle are underlined in the rat sequence. The level of residue conservation is indicated by black (100%), dark grey (70% and more) and light gray (50% and more) background.