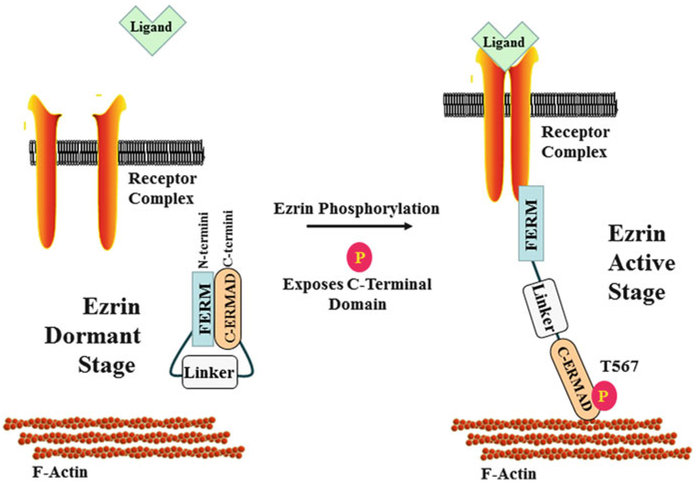
Fig. 2.
Structural regulation of ezrin. Ezrin is normally in a dormant inactive stage with its N-terminal domain interacting and blocking the C-terminal domain. Ezrin is activated by phosphorylation. Ezrin threonine-567 is one of the most characteristic phosphorylation sites, and phosphorylation at threonine-567 causes the dissociation of the intramolecular interaction between the N- and C-terminal domains. This dissociation allows the N-terminal domain to interact with multiple receptor complexes and the C-terminal domain to interact with F-actin. P phosphorylation