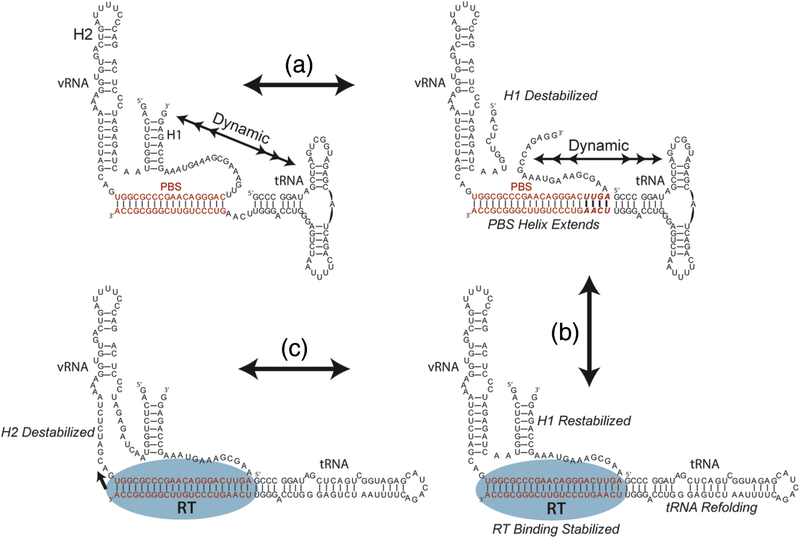
Figure 7.
Model of the early steps of reverse transcription initiation. (a) In the absence of RT, the vRNA-tRNA is structurally dynamic as indicated by multiheaded arrows. Dynamics between formed and melted H1 and the tRNA 5’ end are observed by smFRET. The formation of an extended PBS helix destabilizes H1, and dynamics are still observed between the vRNA 5’ and 3’ ends and the tRNA 5’ end. (b) The binding of reverse transcriptase is stabilized by the extended PBS helix which can make contacts within the RNase H domain, and the dynamic properties of the RNA/RNA complex decrease. Reverse transcriptase binding facilitates refolding of the tRNA into an elongated state and stabilizes H1. (c) The stabilization of H1 may serve to induce strain on H2 which is the RT pause site during the process of initiation.