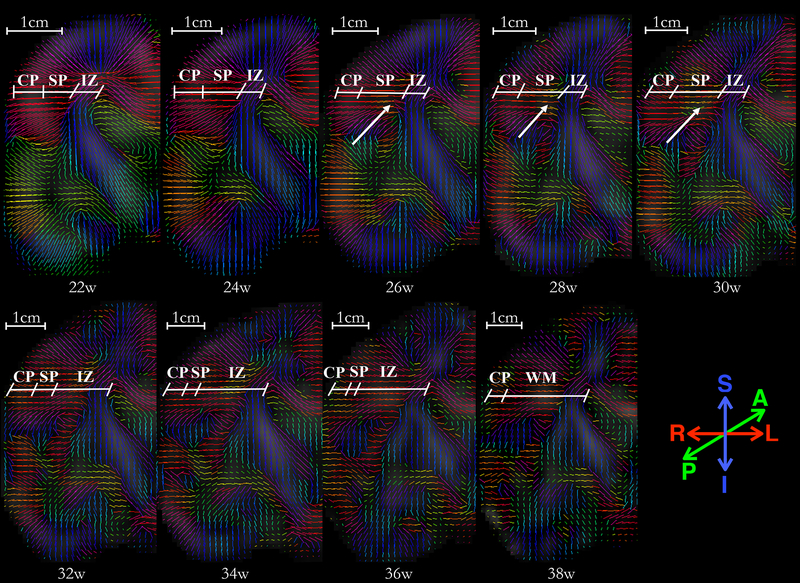
Fig. 10:
A panel of primary eigenvectors of diffusion tensors projected on the right-half coronal plane located in the vicinity of genu of the internal capsule, with inferior section in the temporal lobe and superior section at the boundary of frontal and parietal lobe. Age in gestational weeks is shown below each image. Initial radial organization of cortical plate and subplate, indicated by the primary eigenvectors of the diffusion tensors directed towards the ventricles at 22w, gradually disappears with an increase in gestational age. The reduction in the radial coherence appears to affect various brain regions differently; reduction in inferior region (temporal lobe) appears near-complete at 36 weeks, as compared to the superior region (fronto-parietal lobe) which appears to have significantly reduced radial coherence at GA-34w. Moreover, note that the radial coherence of cortical plate and subplate in central regions, marked at 22w, starts to disappear in regions of deep subplate zone first (26–28w). The reduction in radial coherence parallels appearance of long association fibers (arrows). The borders between transient fetal zones (CP, SP, IZ) were identified in the underlying FA images, and are marked by an oblique line. Abbreviations: cortical plate (CP), subplate (SP), intermediate zone (IZ), and fetal white matter (WM). Borders are approximate and were identified visually on the underlying FA and T2 images by a neuro-anatomist (LV) with expertise in delineating transient fetal zones on MR and histology images.