Figure 6. Thalamic network assignment.
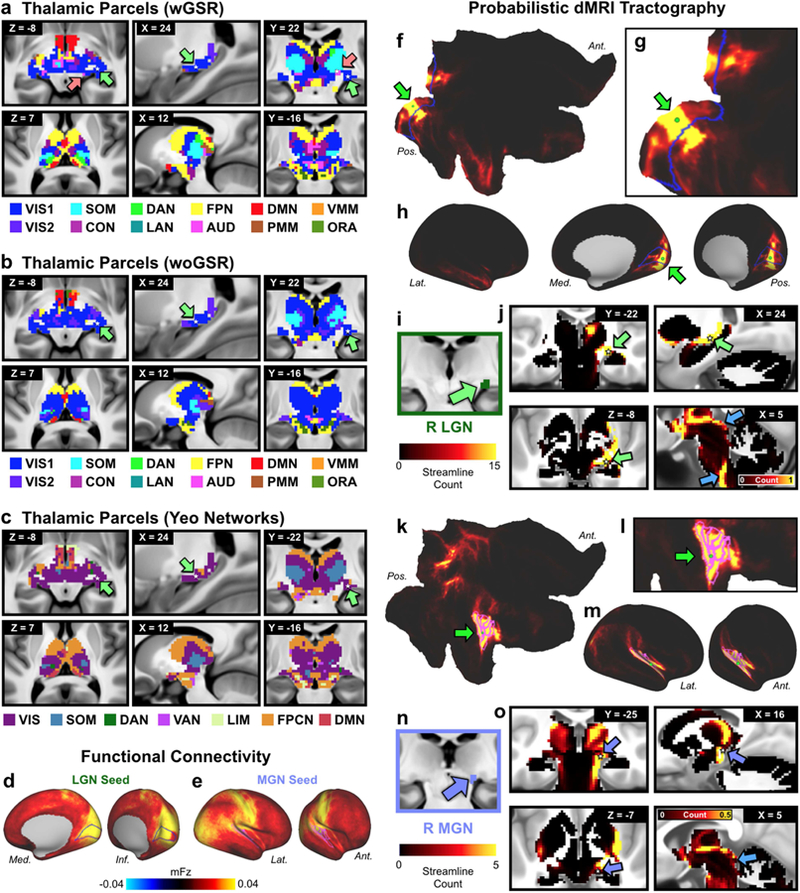
A) Network assignment of the thalamus and ventral diencephalon from the network partition described in the manuscript. Top row highlights the horizontal, sagittal, and coronal views of the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), indicated by green arrows, and the medial geniculate nucleus (MGN), indicated by pink arrows. White stars mark the voxel seeded for functional connectivity in D and E. Bottom row shows cross-sectional view of the parcellation at different slices. B) Network assignment of the thalamus and ventral diencephalon from the parcellation performed without GSR (woGSR). Without GSR, the auditory network assignment of the MGN was not distinguishable in the parcellation. C) Network assignment of thalamus and ventral diencephalon using cortical network parcellation from Yeo et al. (2011). Note the lack of an auditory network in the Yeo et al. (2011) partition limits the ability to map thalamus relative to the new partition reported here. D) Cortical functional connectivity of the bilateral LGN parcels. VIS1 parcels are outlined in blue. Right hemisphere is 26 shown; similar results were seen in the left hemisphere. E) Cortical functional connectivity of the bilateral MGN parcels. AUD parcels are outlined in blue. Right hemisphere is shown; similar results were seen in the left hemisphere. F) Probabilistic tractography (i.e. ‘structural’ connectivity) of the right primary visual cortex (V1) shown in flat cortical map. Seed grayordinate is highlighted with green dot and arrow. Cortical VIS1 network parcels are outlined in blue. Tractography results were computed from diffusion MRI data obtained from the same subjects and averaged over the entire group. G) Magnified view of V1 seed (green dot) in flat cortical map. H) Inflated cortical view of V1-seeded probabilistic tractography results. I) Right LGN identified using the Jülich atlas (Bürgel et al., 2006; Eickhoff et al., 2005), similar coordinates also reported in (Linzenbold et al., 2011; Marx et al., 2004; A. T. Smith et al., 2009). J) Tractography of V1 seed to subcortex, including the right LGN (green arrows). White stars mark the right LGN voxel from which functional connectivity was seeded in D. Connectivity was strongest between V1, right LGN, and other visual processing regions, including the superior colliculus and brainstem nuclei (blue arrows). Results were similar for the left LGN. K) Probabilistic tractography of the right primary auditory cortex, displayed in flat cortical map. Seed grayordinate is highlighted with green dot and arrow. Cortical AUD network parcels are outlined in fuchsia. L) Magnified view of primary auditory seed (green dot) in flat cortical map. M) Inflated cortical view of auditory-seeded probabilistic tractography results. N) Right MGN identified using the Jülich atlas. O) Tractography of primary auditory seed to subcortex, including right MGN (purple arrows). White stars mark the right MGN voxel from which functional connectivity was seeded in E. Connectivity was strongest between right auditory cortex, right MGN, other thalamic nuclei, and auditory processing regions such as the inferior colliculi (blue arrow). Results were similar for the left MGN. Abbreviations: Lat., lateral; Med., medial; Ant., anterior; Pos., posterior.
