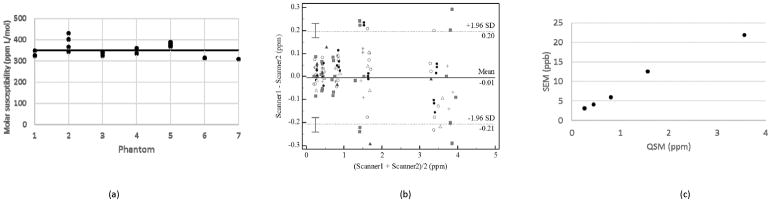
FIG. 3.
Summary statistics and comparisons of QSM data from all scanners. (a) Molar susceptibility estimates obtained as the slope of a linear regression of measured susceptibility values against prepared gadolinium concentrations in each of the seven phantoms. The straight line is the average of all the molar susceptibility values, which is 350 ppm L/mol. b) A Bland-Altman plot of measurements by pairs of scanners for each gadolinium concentration. The limits of agreement were obtained using the method of multiple measurements described by Bland and Altman. Each marker type designates measurements from the same phantom. The maximum difference between measurements can be seen to increase from less than 0.1 ppm for measurements for average measurements of 0.21 ppm to more than 0.2 ppm for average measurements of 3.36 ppm. (c) Plot of the standard error of measurement (SEM) against the QSM measurement. The SEM increases from 3.1 ppb to 21.9 ppb, as the gadolinium concentration increases.