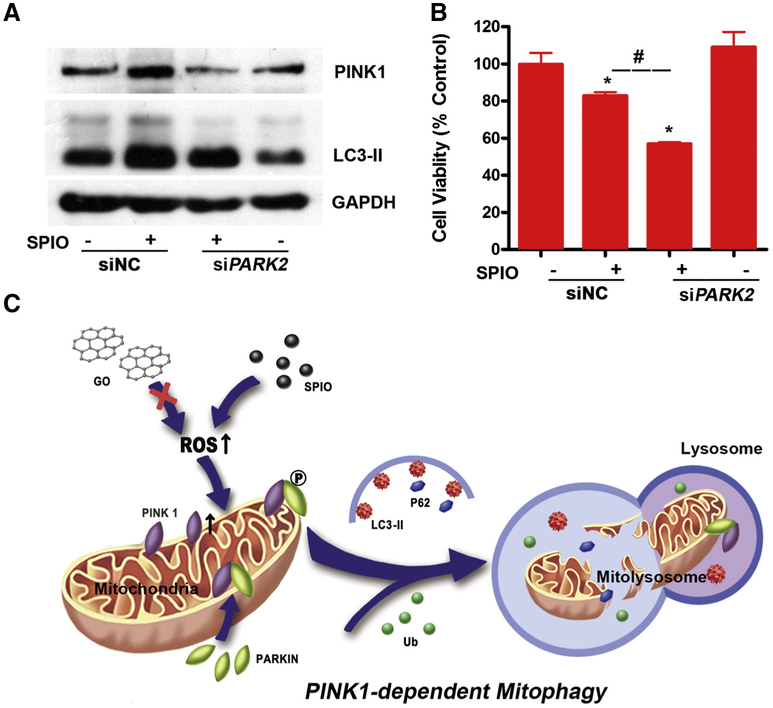
Figure 6.
Knockdown of PARK2 aggregates SPIO-NPs-induced mitophagy and cytotoxicity of L02 cells. (A) Knockdown of PARK2, with transfection 50 nM siRNA for 12 h, decreased the up-regulation of the PINK1 and LC3-II induced by SPIO-NPs using Western blot. GAPDH was used as loading control. (B) Knockdown of PARK2 exacerbated the decrease of cell viability caused by SPIO-NPs using MTS assay. siNC stands for the siRNA negative control. All data are expressed as mean ± SD of four replicates. * P<0.05, compared to siNC; # P<0.05, compared to the SPIO-NPs-treated group. (C) The scheme of this study. SPIO-NPs, but not GO-QDs, trigger ROS overproduction and mitochondrial disrupt in hepatic cells, leading to the increase in PINK1 stability. PINK1 then recruits and phosphorylates PARKIN at Ser65. The p-PARKIN ubiquitinates the proteins at mitochondrial outer membrane and recruits the ubiquitins (Ub) to the damaged mitochondria that fuse into lysosomes with the help of LC3-II and P62, and finally making mitochondria go through mitophagy.