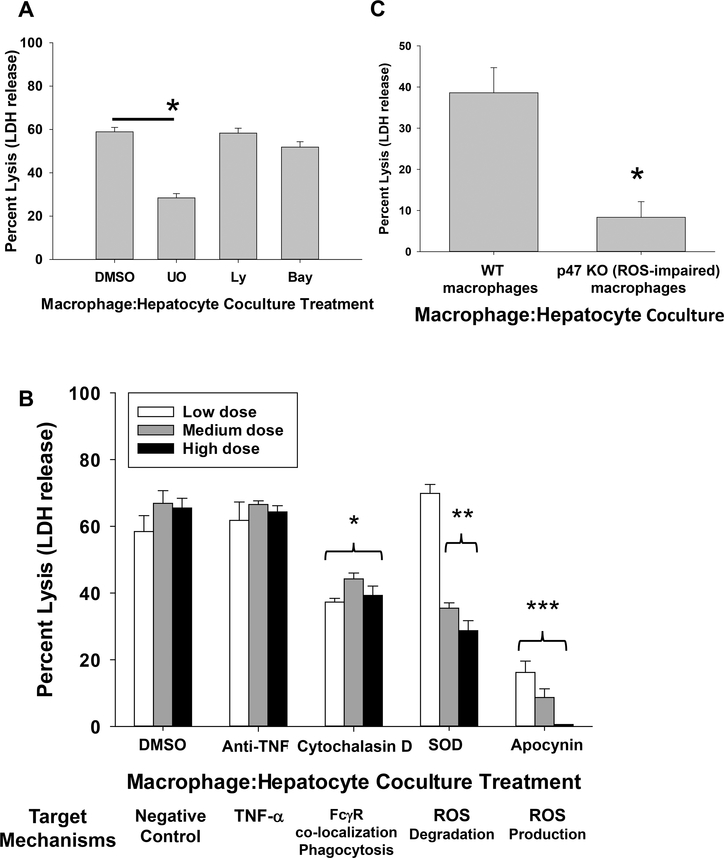
Figure 4. In vitro macrophage-mediated hepatocytotoxicity is reactive oxygen species-dependent.
All macrophage:hepatocyte co-cultures consisted of FVB/N hepatocytes, activated macrophages and alloserum. RAW 264.7 macrophages and BMM were activated by pretreatment with IFN-γ (2.5 ng/mL; 18 hours). A) During co-culture of hepatocytes and RAW macrophages, cultures were treated with DMSO control, UO126, LY294002, or BAY11–7058. While treatment with LY294002 (58.3±2.3%; n=12, 20 μM; p=ns) and BAY11–7085 (51.9±2.5%; n=12, 5 μM, p=ns) did not inhibit macrophage-mediated hepatocytotoxicity compared to positive control (58.9±2.1%; DMSO control, n=20), treatment with UO126 (28.4±2.0%; n=14, 5 μM; p<0.0001, as denoted by “*”) significantly inhibited macrophage-mediated cytotoxicity of alloantibody-incubated hepatocytes. Data is combined from triplicate experiments. B) In a separate cohort, co-cultures were incubated with DMSO (vehicle control), anti-TNF-α mAb, cytochalasin D, superoxide dismutase (SOD), or apocynin. Both superoxide dismutase (200 U/mL= 69.8±2.7%; 500 U/mL= 35.4±1.6%; 1,000 U/mL=28.7±3.0%; n=4 for all, p<0.0005 for 500 and 1,000 U/mL, as denoted by “**”) and apocynin (0.25 mM=16.9±4.0%; 0.5 mM=9.6±3.0%; 1.0 mM=0±0%; n=5 for all, p<0.0001 for all, as denoted by “***”) significantly inhibited macrophage-mediated hepatocytotoxicity (apocynin abrogated cytotoxicity at 1.0 mM) as compared to DMSO-treated co-cultures (0.1%=62.6±3.3%, 0.5%= 66.9±3.8%, 1.0%= 65.5±2.9%; n=6 for all). RAW cells incubated with anti-TNF-α mAb at all doses tested (5 μg/mL=61.8±5.5%; 10 μg/mL=66.6±1.1%; 20 μg/mL=64.3±1.9%; n=4 for all) had no effect on macrophage-mediated hepatocytotoxicity. Cytochalasin D (inhibitor of actin polymerization and FcγR co-localization) significantly impaired macrophage-mediated hepatocytotoxcity (1 μg/mL=37.3±1.1%; 5 μg/mL=44.2±1.8%; 10 μg/mL=39.3±2.8%; n=4 for all, p<0.009 for all doses, as denoted by “*”). Data is combined from duplicate experiments. C) Bone marrow macrophages (BMM) were isolated from WT and p47 KO mice and co-cultured with allogeneic hepatocytes and alloserum. Macrophage-mediated hepatocytotoxicity was significantly impaired in co-cultures containing p47-deficient BMM (8.3±3.8%; n=6) which cannot produce ROS compared to WT BMM (38.6±6.1%; n=6, p=0.0009, as denoted by “*”). Data is combined from duplicate experiments.