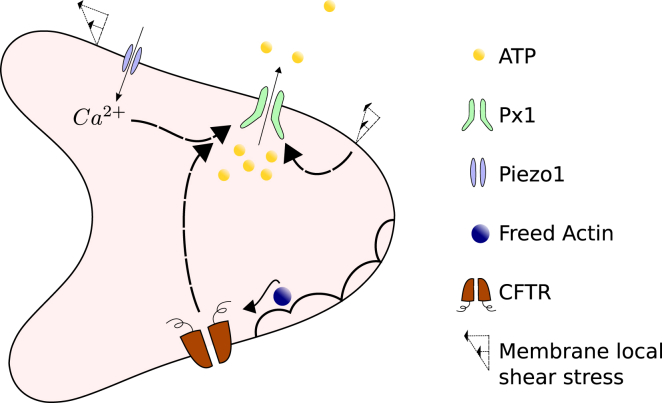
Figure 3.
Schematics of the ATP release pathway in RBC: Px1 is the main avenue for ATP release that can be activated by the local shear stress and Ca2+ ions; the Piezo1 cation channel can be activated by the local shear stress and trigger Ca2+ influx; actin is freed from deformation-induced cytoskeletal defects; CFTR is activated by freed actin and consequently upregulates Px1. To view this figure in color, go online.