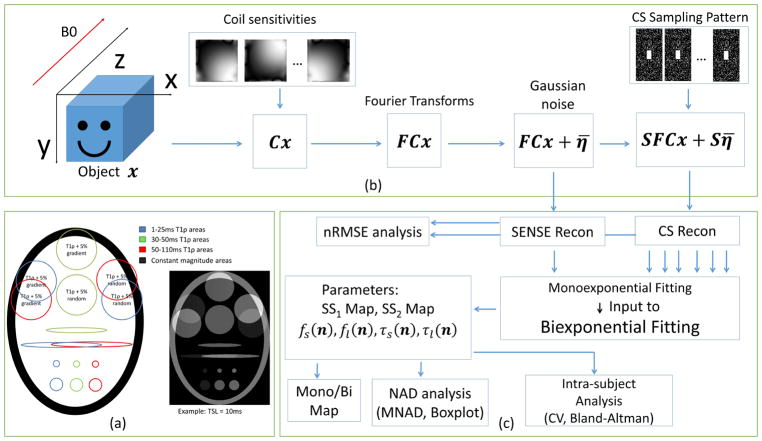
Figure 1.
(a) Synthetic phantom utilized in the experiments, composed of three areas with different T1ρ time ranges. The T1ρ relaxation times were randomly selected from the ranges 1–25ms, 30–50ms, and 50–110ms, intersections generate a biexponential signal. (b) MRI acquisition model used for CS reconstructions, including coil sensitivities C, Fourier transform F, and k-space undersampling pattern S using Poisson disk with fully-sampled central area, also additive white Gaussian noise η̄. (c) Diagram of the process, including reconstruction, fitting, mono/biexponential detection, reconstruction and fitting error analysis and intra-subject analysis.