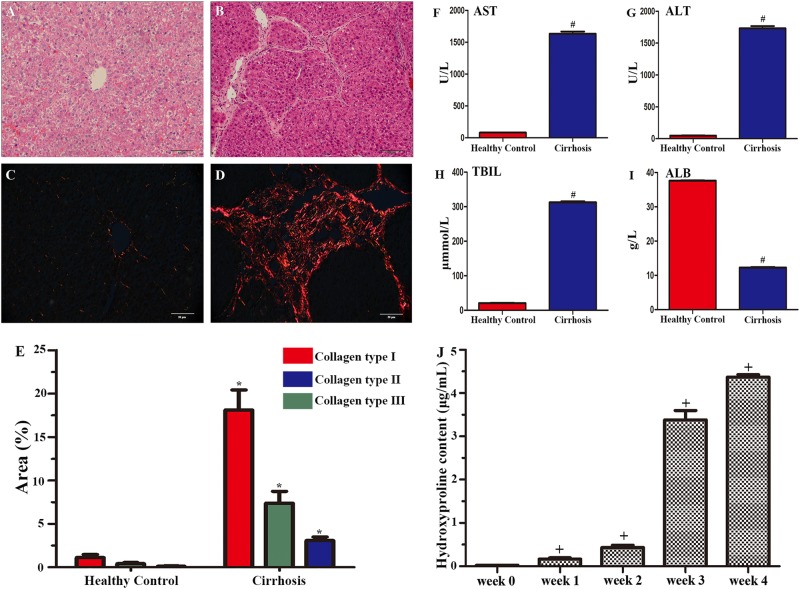
Fig. 1. Histological analysis, serological characterisation and hydroxyproline determination of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver injury.
a and b show H&E staining of liver tissues from a healthy control a and a CCl4-treated rat b 4 weeks after model induction. Picrosirius red staining in liver sections from a healthy control and a rat with cirrhosis 4 weeks after model induction c, d. Quantitative analysis of fibrillary collagen showed significant increases, with the highest increase in collagen type I, compared with that in healthy controls e. Scale bar = 50 μm in a applied to b–d. All the data are displayed as the means ± SDs; n = 4 for each group, *p < 0.05 vs. healthy controls. f–i show dramatic increases in serum alanine aminotransferase (AST) f, aspartate aminotransferase (ALT) g and total bilirubin (TBIL) h in the CCl4-treated rats. In contrast, serum levels of albumin (ALB) were lower in the CCl4-treated group than the control group i. All the data are displayed as the means ± SDs; n = 5 for each group, #p < 0.001 vs. healthy controls. j shows dramatic increases in serum hydroxyproline content in 4 weeks. All the data are displayed as the means ± SDs the data; n = 5 for each group, +p < 0.001 vs. week 0