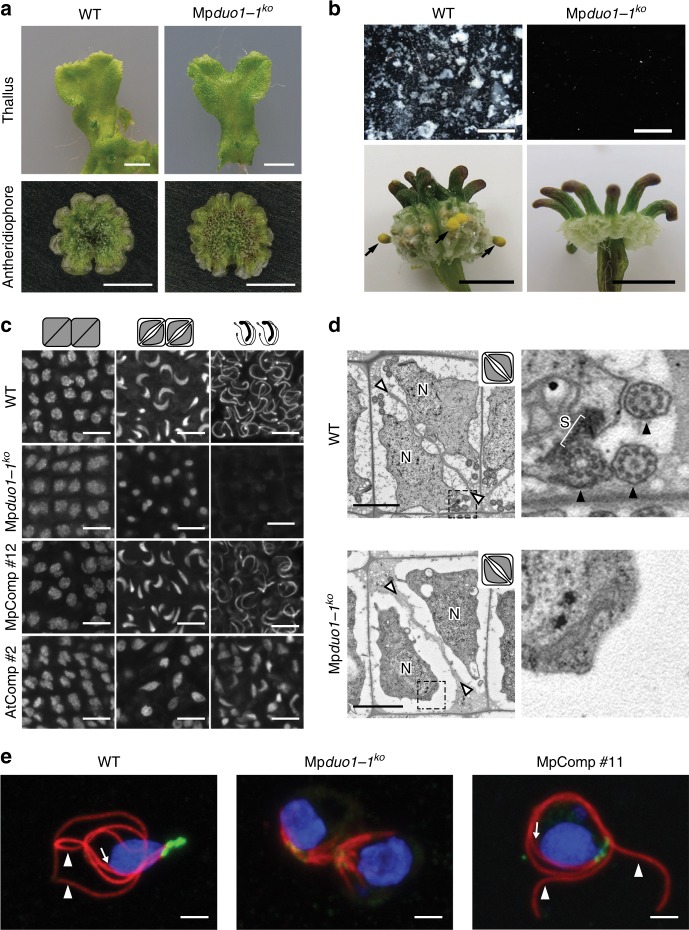
Fig. 2.
Mpduo1-1ko shows defects in sperm morphogenesis. a Images of thallus (top) and antheridiophore (bottom) of WT (left) and Mpduo1-1ko (right). b Top panels show sperm masses (white) discharged from mature antheridiophores into water in WT but not in Mpduo1-1ko. Bottom panels show the production of yellow sporangia (black arrows), which mark successful fertilization, on female WT about a month after crossing with male WT, but no sporangia production in crosses with male Mpduo1-1ko. c Feulgen staining of spermatids during spermiogenesis in WT, Mpduo1-1ko, and Mpduo1-1ko complemented by MpDUO1 genomic fragment (MpComp) and by proMpDUO1:AtDUO1 (AtComp). d Transmission electron micrographs of spermatids. White arrowheads indicate cell boundaries and N indicates nucleus. Areas in the dashed line boxes are enlarged in the right panels and show that the spline (S), a microtubular backbone-like structure, and flagella (black arrowheads) are present in WT but missing in Mpduo1-1ko. e Localization of centrins (green) and tubulins (red) in differentiating spermatids of WT, Mpduo1-1ko (the panel shows two sister cells), and MpComp. Centrin signals mark two basal bodies and an associated multi-layered structure. The blue signals indicate the DAPI stained nuclei. White arrowheads and arrows indicate flagella and spline, respectively. Scale bars, 5 mm (a), 400 μm (b, top), 5 mm (b, bottom), 5 μm (c), and 2 μm (d, e)