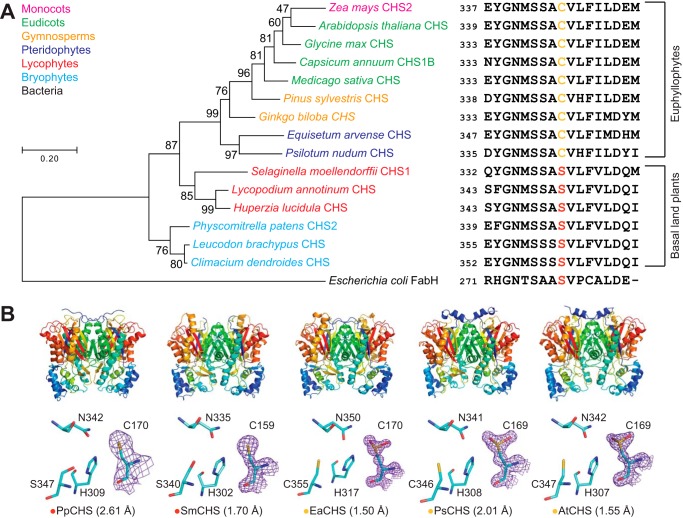
Figure 2.
Structural and in vivo functional characterization of diverse CHS orthologs. A, maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree of CHSs from diverse land-plant species, with clades indicated by color. The tree is rooted on a bacterial KAS III enzyme (EcFabH). The scale bar indicates evolutionary distance in substitutions per amino acid. The sequence near the differentially conserved cysteine/serine (position 347 in AtCHS) is shown for each CHS. B, overall apo crystal structures and active-site structures of CHSs from diverse plant lineages. Top, the homodimeric form of CHS is shown with a color gradient from blue at the N terminus to red at the C terminus of each monomer. Bottom, backbone and side chains of the catalytic triad and the differentially conserved cysteine/serine are shown. The 2Fo − Fc electron density map contoured at 1.5σ is shown around the catalytic cysteine. CHSs from euphyllophytes show the catalytic cysteine oxidized to sulfinic acid, whereas CHSs from basal land plants have a reduced catalytic cysteine. The red or yellow dot next to the enzyme name indicates the presence of serine or cysteine, respectively, in position 347 (AtCHS numbering).