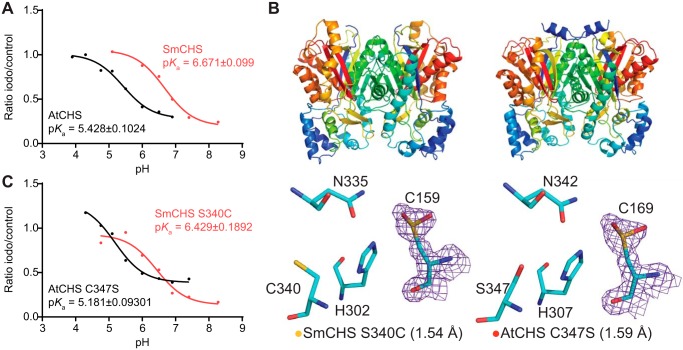
Figure 3.
pKa measurement of the catalytic cysteine and characterization of key residues that affect pKa. A, pKa measurement of AtCHS and SmCHS WT enzymes. CHS enzyme was pre-incubated at various pH values with or without the 25 μm iodoacetamide inhibitor for 30 s, and an aliquot was taken to run in a CHS activity assay. The ratio of naringenin product produced in the iodoacetamide treatment divided by the control treatment was calculated for each pH point. A nonlinear regression was performed to fit a log(inhibitor) versus response curve to determine the pH at which 50% of maximal inhibition was achieved, which was determined to be the pKa value of the catalytic cysteine residue. The pKa of AtCHS is close to the 5.5 determined for other euphyllophyte CHSs, whereas the pKa of SmCHS is over 1 pH unit higher. B, overall structures and active-site configurations of AtCHS C347S and SmCHS S340C single mutants. The 2Fo − Fc electron density map contoured at 1.5σ is shown around the catalytic cysteine. SmCHS S340C shows oxidation of Cys-159, unlike the SmCHS WT. AtCHS C347S has an oxidized Cys-169, like AtCHS WT. C, pKa measurements of AtCHS C347S and SmCHS S340C mutants.