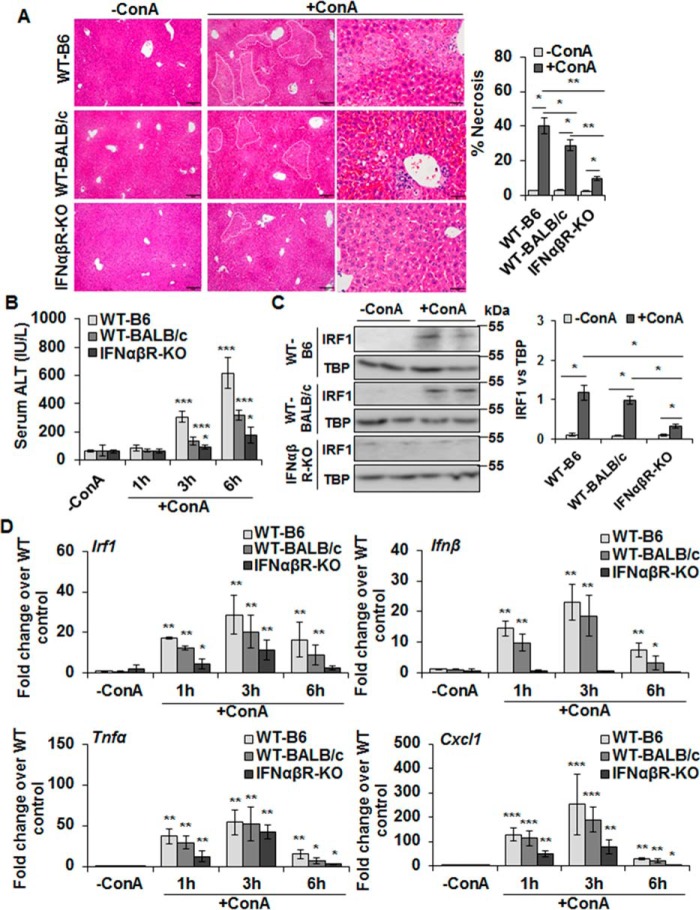
Figure 4.
ConA-induced hepatic injury in IFNαβR-KO mice. A, mice were euthanized 6 (WT-B6) or 8 h (WT-BALB/c or IFNαβR-KO) after administering 20 mg/kg of ConA. Representative sections of the vehicle- or ConA-treated livers stained with hematoxylin/eosin (H/E) show protection in IFNαβR-KO mice compared with WT controls. Bar graph shows quantification of necrotic area as defined in the H/E-stained liver sections. Scale bars, 100 μm (left and middle panels) and 50 μm (right panels). B, mice were euthanized 1, 3, or 6 h after administering 20 mg/kg of ConA. ConA-treated IFNαβR-KO mice show significantly lower serum ALT levels as compared with the WT mice. Data are expressed as mean ± S.D. n = 4–6 mice/group. C, Western blotting of the nuclear lysates shows IRF1 in WT (B6 and BALB/c) and IFNαβR-KO mice. Bar graph shows the relative densitometry values normalized to TBP as an internal control (n = 4–6 mice/group). D, mRNA expression of the indicated mediators in ConA-challenged mice at 1, 3, or 6 h as measured via qRT-PCR. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.005; ***, p < 0.0005.