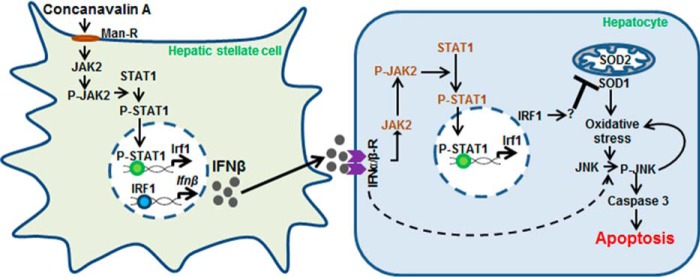
Figure 8.
Schematic illustration of mechanism of ConA-induced liver injury. ConA binding to the mannose 6-phosphate receptor (Man-R) on HSCs induces JAK2 phosphorylation, which then phosphorylates STAT-1. The activated STAT1 translocates into the nucleus and induces IRF1 transcription. IRF1 produced this way stimulates IFNβ transcription. IFNβ protein released by HSCs binds to the IFNαβ receptor on hepatocytes and instigates JAK2/STAT1 activation, followed by IRF1 synthesis. IRF1 (through as yet unidentified mechanism) inhibits SOD expression leading to oxidative stress. Oxidative stress as well as IFNαβ stimulate JNK and caspase 3 activation, and cause apoptosis of hepatocytes.