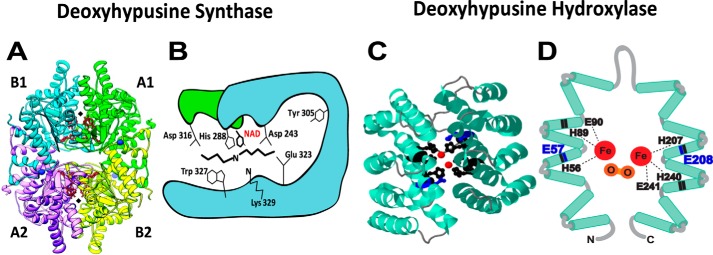
Figure 3.
Crystal structures of DHPS and DOHH and their active sites. A, human DHPS homotetramer (PDB codes 1ROZ and 1RLZ) complex with NAD (41). The two active sites at the dimer interfaces are indicated by black diamonds. B, active site residues of DHPS critical for catalysis (Lys329 and His288) and binding of spermidine (Asp243, Asp316, Glu323, and Trp327) (23, 42). C, crystal structure of DOHH peroxo–diiron intermediate (PBD code 4D4Z) (50) consisting of eight HEAT repeats (helical hairpins), diiron center (red), and critical active-site residues (black and blue). D, a diagram of DOHH (11) active site showing peroxo (orange)–diiron (red) center and the four conserved His-Glu motifs critical for catalysis. His56, His89, Glu90, His207, His240, and Glu241 (black) are required for the binding of iron (49), and Glu57 and Glu208 (blue) are required for binding of the terminal amino group of deoxyhypusine side chain (blue) (53).