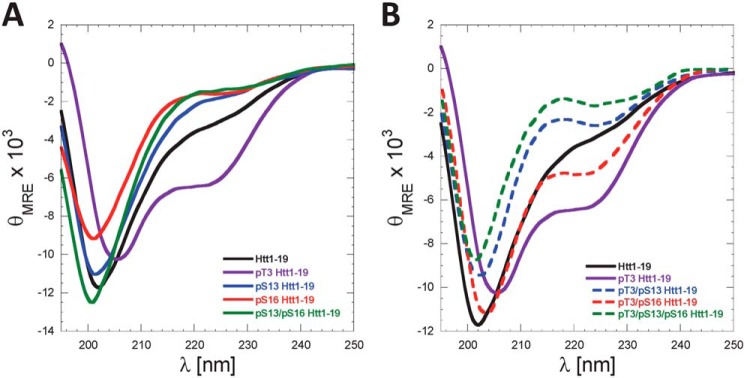
Figure 8.
Serine phosphorylation at Ser-13 and/or Ser-16 disrupts the amphipathic α-helix of Nt17 and reverses pThr-3–induced α-helix formation of Nt17. A, far-UV CD spectra (θMRE = mean residue ellipticity) of Htt1–19 peptides bearing single (pThr-3, pSer-13, or pSer-16) or multiple phosphorylated (pSer-13/pSer-16) residues at 60 μm (pH 7.4). A, phosphorylation of Thr-3 increases the helicity of Nt17, whereas phosphorylation at Ser-13, Ser-16, or both residues reduces the helical propensity of Nt17. B, phosphorylation at Ser-13, Ser-16, or both residues disrupts pThr-3–induced α-helix formation of Nt17. To allow for better visualization and comparison of the data and the effect of phosphorylation at Ser-13 and/or Ser-16 on pThr-3–induced α-helix formation, the far-UV CD spectra of Htt 1–19 and Htt 1–19 pThr-3 were replotted again in B.