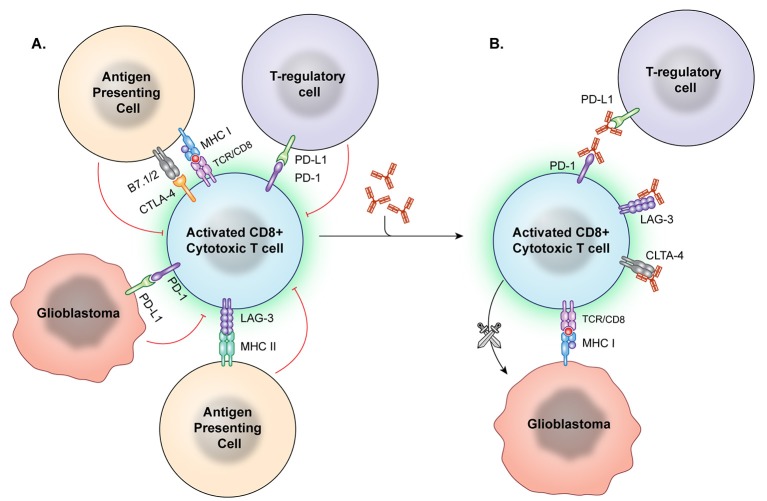
Figure 2.
Immune checkpoint inhibition. (A) Immune checkpoints hinder T-cell activation and promote an immunosuppressive state. However, these checkpoint molecules can be neutralized by targeted antibodies. (B) After the checkpoint molecules are negated by these blocking antibodies, T effector cells are better able to recognize and attack tumor cells.