FIGURE 2.
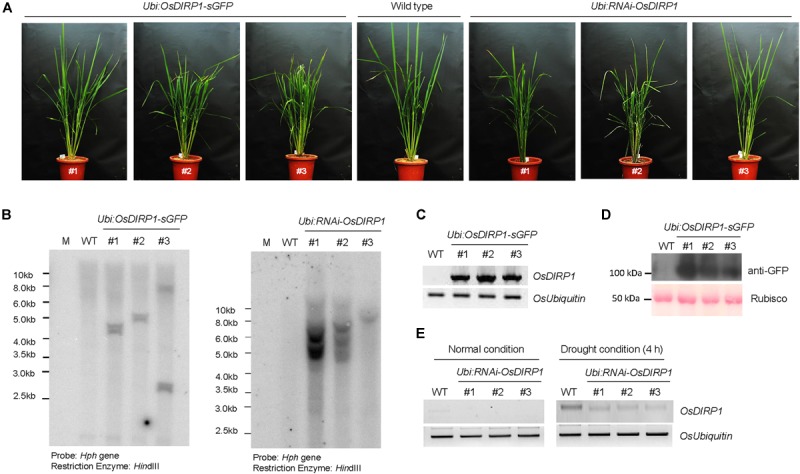
Molecular characterization of OsDIRP1-overexpressing and RNAi-mediated knock-down transgenic rice plants. (A) Morphology of 2-month-old wild-type (WT), T4 Ubi:OsDIRP1-sGFP, and T4 Ubi:RNAi-OsDIRP1 rice plants grown under long-day conditions (16 h light and 8 h dark). (B) Genomic Southern blot analysis. Total leaf genomic DNA was isolated from wild-type (WT), T4 Ubi:OsDIRP1-sGFP (lines #1, #2, and #3), and T4 Ubi:RNAi-OsDIRP1 (lines #1, #2, and #3) rice plants. The DNA was digested with HindIII and hybridized to a 32P-labeled hygromycin B phosphotransferase (Hph) probe under high stringency conditions. (C) RT-PCR analysis of the wild-type (WT) and T4 Ubi:OsDIRP1-sGFP (independent lines #1, #2, and #3) transgenic rice plants to examine OsDIRP1 transcript levels. OsUbiquitin was used as a loading control. (D) Immunoblot analysis of wild-type (WT) and T4 Ubi:OsDIRP1-sGFP plants. Total proteins were isolated using 2x SDS sample buffer and immunoblotted with anti-GFP antibody. Rubisco was used as an equal loading control. (E) RT-PCR analysis of the wild-type (WT) and T4 Ubi:RNAi-OsDIRP1 plants. RNA was isolated from whole seedlings of non-drought-treated (0 h) and drought-treated (4 h) wild-type (WT) and Ubi:RNAi-OsDIRP1 (lines #1, #2, and #3) plants. OsUbiquitin was used as a loading control.
