Figure 2. Pan-PIM kinase inhibitor and lenalidomide combination resulted in more effective anti-myeloma activity in vivo in subcutaneous xenograft myeloma model.
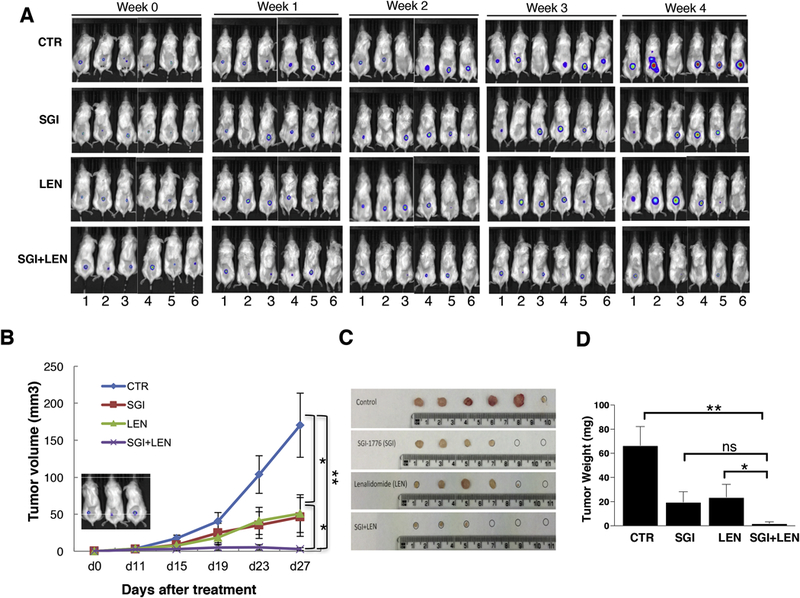
MM1R cells stably expressing luciferase (1.5×106 cells/mouse) were injected subcutaneously into the back of sublethally irradiated (1.5Gy) NSG mice. Tumor growth was followed weekly by bioluminescence imaging. At day 10 of cell injection, mice were treated (indicated as Week 0 in A and day 0 in B) with either: DMSO, SGI1776 (35mg/kg body weight), lenalidomide (25mg/kg body weight), or the combination of SGI1776 and lenalidomide by daily oral gavage. A and B: The combination of SGI1776 and lenalidomide is more effective in anti-myeloma activity. A: Bio-luminescence imaging; B: Tumor volume. The inset panel showed myeloma tumor establishment measured by bioluminescent imaging just before the treatment. C and D: Tumor was significantly reduced in mice treated with a combination of SGI1776 and lenalidomide. C: Tumor size; D: tumor weight. (ns: no statistically significant; *: p<0.05; **: p< 0.01)
