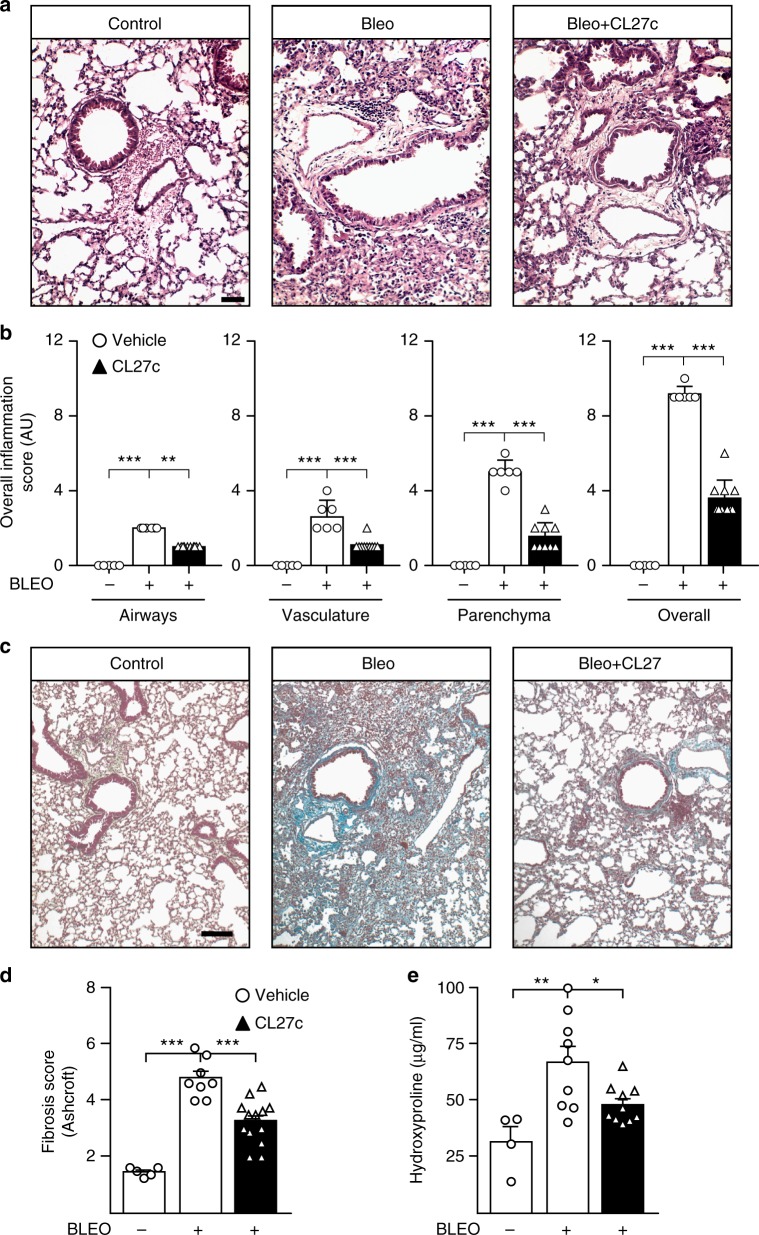
Fig. 7.
CL27c attenuates inflammatory and fibrotic processes in a moderate protocol of bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. a Representative hematoxylin- and eosin-stained lung tissues depicting that aerosolized CL27c (2 mg/ml) reduced Bleomycin (2 mg/kg)-elicited tissue injury and inflammatory cells accumulation. Bar = 25 µM b Histopathologic scoring of inflammatory damage in lung sections derived from control (Bleo−) and Bleo-treated mice (Bleo+) with and without treatment with CL27c (black and white bars, respectively) (from left to right, airways n = 5, 5, 10, vasculature n = 5, 6, 10, parenchyma n = 5, 6, 9, and overall n = 5, 6, 10 independent experiments, respectively). c Representative Gomori’s trichrome-stained sections showing that treatment with CL27c reduced lung fibrosis, remodeling, alveolar walls, and collagen deposition (green). Bar = 100 µm. d Quantification of fibrosis on lung sections using the semi-quantitative Ashcroft scale (from left to right n = 5, 8, 10 independent experiments, respectively). e Analysis of hydroxyproline deposition (from left to right n = 4, 9, 10 independent experiments, respectively). Results represent mean ± s.e.m., *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 determined using either Kruskal–Wallis followed by Dunn’s test (b) or one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test (d, e)