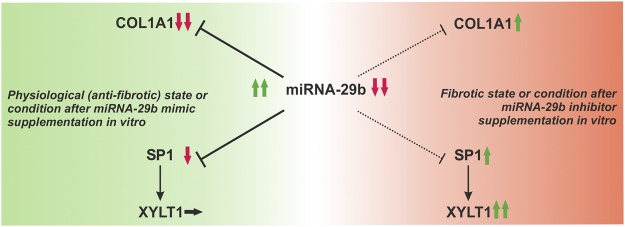
Figure 8.
Hypothetical model of XYLT1 regulation via miRNA-29b. Physiologically, miRNA-29b suppresses the expression levels of COL1A1 and SP1, which are direct targets of the miRNA. Suppression of COL1A1 and SP1 goes along with anti-fibrotic remodeling, which is also achieved by using miRNA-29b mimics in vitro. Sp1 is known to stimulate XYLT1 mRNA expression, but the XYLT1 expression might not be affected by an SP1 decrease due to the availability of several other influencing transcription factors and mediators (left side). The miRNA-29b level is diminished in fibrosis. This state is reproducible by using miRNA-29b inhibitors in vitro. A decrease in miRNA-29b implies a minor inhibition of COL1A1 and SP1 mRNA expression, which can contribute to COL1A1 and SP1 upregulation. Sp1 upregulation provokes a XYLT1 induction (right side). Aside from XYLT1 regulation via Sp1, additional mechanisms might exist which have not yet been elucidated.