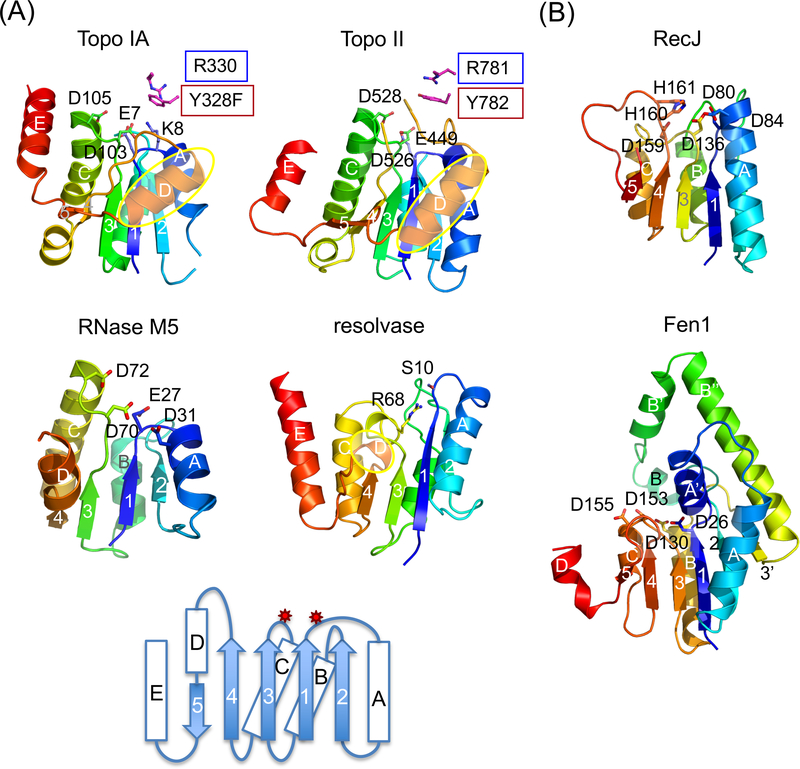
Fig. 4.
TOPRIM and SR catalytic domain are similar in the folding topology and active-site location. (a) TOPRIM domain of Topo IA (1I7D), II (2RGR) and RNase M5 (1T6T) are aligned with the catalytic domain of γδ resolvase (1GDT). Each is shown in rainbow-colored ribbon diagrams. Active site residues are highlighted as sticks. The D helices (in yellow ovals) in topoisomerases are longer than in resolvase. A topology diagram below summarizes all four examples. The catalytic residues are located on two loops indicated by the red stars. Three carboxylates (E, DxD) are conserved among all TOPRIM domains for metal-ion binding. M5 nuclease has an additional carboxylates (D31) and uses water as nucleophile. Topo IA has a catalytic Lys (K8) in the equivalent location. (b) Ribbon diagrams of the catalytic domain of RecJ (1IR6) and Fen1 (1EXN) in rainbow colors. The catalytic residues are shown and labeled. Inserted elements in Fen1 are labeled after the adjacent secondary structures with apostrophes (A’, B’, B” and 3’).