Figure 5.
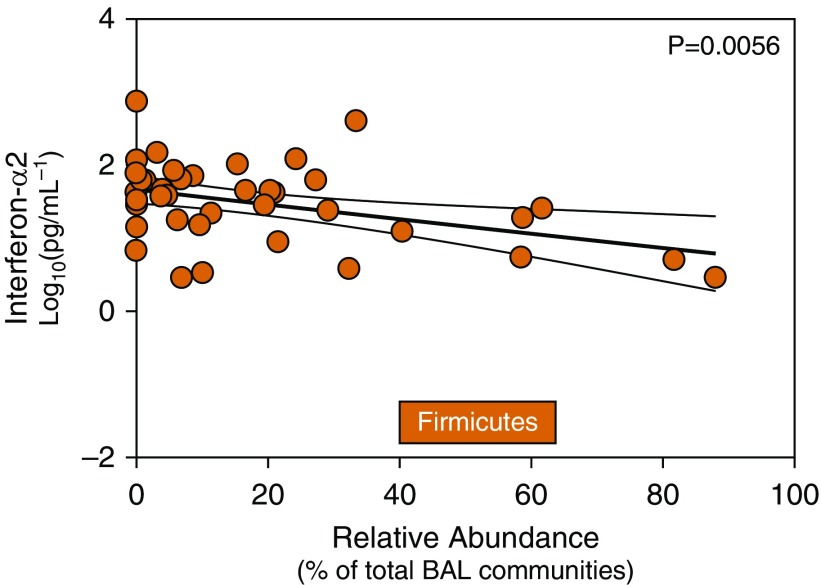
Pulmonary microbiota correlate with changes in alveolar IFN-α2. To examine possible associations between alveolar inflammation and pulmonary microbiota, we analyzed microbiota at a phylum level with alveolar T-helper cell type 1 cytokines by linear regression. We found significant associations between alveolar cytokines and lung microbiota in hematopoietic cell transplant recipients. Relative abundance of the Firmicutes phylum was negatively associated with alveolar concentrations of IFN-α2 (adjusted P value = 0.0073). Correlations are made using linear regression of relative abundance microbiota data and logarithmically transformed cytokine data. Results depicted are from univariate linear regression modeling with regression line and confidence intervals.